Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why did Mendel choose pea plants for conducting his experiments on inheritance?
Solution
Mendel chose pea plants for studying inheritance because of the following reasons:
- Pea plants had a number of clear cut differences which were easy to tell apart. For example, some pea plants were 'tall' whereas others were 'dwarf'.
- They were self pollinating plants.
- Many generations of pea plants can be produced in a comparatively short time span and their study is much simpler than that of animals.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How did Mendel interpret his results to show that traits may be dominant or recessive? Describe briefly.
In a monohybrid cross between tall pea plants (TT) and short pea plants (tt), a scientist obtained only tall pea plants (Tt) in the F1 generation. However, on selfing the F1 generation pea plants, he obtained both tall and short plants in F2 generation. On the basis of above observations with other angiosperms also, can the scientist arrive at a law? If yes, explain the law. If not, give justification for your answer.
Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs.
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding pea plants bearing violet flowers with pea plants bearing white flowers. What will be the result in F1 progeny?
It it an example of monohybrid cross or dihybrid cross?
Give the contrasting traits of the following characters in pea plant and mention which is dominant and which is recessive :
Round seed
State Mendel's second law of inheritance.
Pure-bred round-yellow pea seeds have genotype RRYY and the pure-bred wrinkled-green pea seeds have genotype rryy. Keeping this in mind, write the phenotypes of the following genotypes of hybrid pea seeds :
(a) Rryy
(b) rrYy
(c) rrYY
(d) RrYy
(e) RRyy
Answer the following question.
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and F2 generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F2 generation plants.
In the following figure showing a germinating gram seed, name the parts labelled as A, B and C:
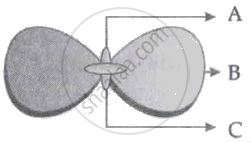
Why is Part 'B' considered to be important during germination?
