Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How do Mendel’s experiments show that the traits may be dominant or recessive?
उत्तर
Mendel crossed purebred tall pea plants with purebred dwarf pea plants and found that only tall pea plants were produced in the first generation, and there were no dwarf pea plants. He concluded that the first generation showed the traits of only one of the parent plants tallness. The trait of the other parent plant dwarfness did not show up in the progeny of the first generation.
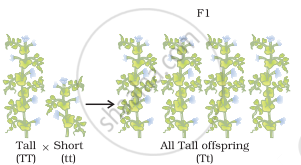
He then crossed the tall pea plants obtained in the first generation (F1 generation) and found that both tall plants and dwarf plants were obtained in the second generation (F2 generation) in the ratio of 3 : 1. Mendel noted that the dwarf trait of the parent pea plant which disappeared in the first generation progeny reappeared in the second generation. In this way, Mendel’s experiments with tall and dwarf pea plants showed that the traits may be dominant and recessive.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How do Mendel's experiment show that traits are inherited independently?
The gene for red hair is recessive to the gene for black hair. What will be the hair colour of a person if he inherits a gene for red hair from his mother and a gene for black hair from his father?
Using height (tallness/dwarfness) of a plant as an example, show that genes control the characteristics or traits in an organism.
In the F2 generation of a cross, progeny having different traits are produced in the ratio 3 : 1. State whether it is a monohybrid cross or a dihybrid cross? Give one example of such a cross.
State Mendel's second law of inheritance.
How do Mendel's experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
When two parents are crossed, the offspring are referred to as :
recessives
test cross
F1 generation
F2 generation
A cross between two individuals results in a ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 for four possible phenotypes of progeny. This is an example of a ______
In order to ensure that he had pure-breeding plants for his experiments, Mendel :
(a) cross-fertilised each variety with each other
(b) let each variety self fertilise for several generations
(c) removed the female parts of the plants
(d) removed the male parts of the plants.
The visible characteristic in an organism is known as :
(a) prototype
(b) stereotype
(c) phenotype
(d) genotype
A trait in an organism is influenced by ______
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes. What will be the colour of eyes of the persons having the following combination of genes?
(a) Bb
(b) bb
(c) BB
The term 'father of genetics' is used for the scientist :
(a) Morgan
(b) Mendel
(c) Darwin
(d) Marie Curie
Answer the following question.
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F1 and F2 generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F2 generation plants.
In human males all the chromosomes are paired perfectly except one. This/these unpaired chromosome is/are
- large chromosome
- small chromosome
- Y-chromosome
- X-chromosome
What are the components of the DNA molecule?
If a tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant then, what percentage of F1 and F2 generation respectively will be tall?
A cross between pea plant with white flowers (vv) and pea plant with violet flowers (VV) resulted in F2 progeny in which ratio of violet (VV) and white (vv) flowers will be ______.
