Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Describe in brief the cleansing action of soap.
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Solution 1
Cleansing action of soaps:
The dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and is insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by only washing with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water and, thus, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.

Solution 2
The cleaning action of soap can be described as follows:
- A soap molecule has a tadpole-shaped structure.
- At one end (long, non-polar end) of the soap molecule is a hydrocarbon chain which is insoluble in water but soluble in oil.
- At the other end (short polar end) of the soap molecule, there is a carboxylate ion which is hydrophilic, i.e. water soluble but insoluble in oil.
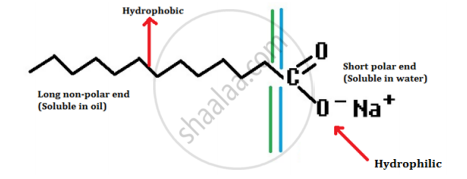
- Soap, on mixed with water, forms a concentrated solution and causes foaming.
- The long non-polar end of soap gravitates towards and surrounds the dirt and absorbs the dust in it.
- The short polar end with the carboxylate ion repels the water away from the dirt.
- A spherical aggregate of soap molecules is formed in the soap solution in water and is called a micelle.
- Thus, the soap molecule dissolves the dirt and our clothes get clean.
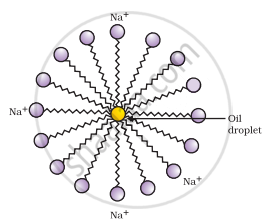
Formation of micelles
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Differentiate between Toilet soap and Laundry soap.
Which of the following sets of materials can be used for conducting a saponification reaction for the preparation of soap?
(a) Ca(OH)2 and neem oil
(b) NaOH and neem oil
(c) NaOH and mineral oil
(d) Ca(OH)2 and mineral oil
A student takes four test tubes marked P, Q, R and S of 25 mL capacity and fills 10 mL of distilled water in each. He dissolves one spoon full of four different salts in each as − KCl in P, NaCl in Q, CaCl2 in R and MgCl2 in S. He then adds about 2 mL of a sample of soap solution to each of the above test tubes. On shaking the contents of each of the test tubes, he is likely to observe a good amount of lather (foam) in the test tubes marked
(a) P and Q
(b) R and S
(c) P, Q and R
(d) P, Q and S
Hard water is not available for an experiment. Some salts are given below :
(I) Sodium chloride
(II) Sodium sulphate
(III) Calcium chloride
(IV) Calcium sulphate
(V) Potassium chloride
(VI) Magnesium sulphate
Select from the following group of these salts, each member of which may be dissolved in water to make it hard.
(A) I, II, V
(B) I, III, V
(C) III, IV, VI
(D) II, IV, VI
What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
State one advantage of soaps over detergent.
Explain the process of preparation of soap in laboratory.
Why is soap not suitable for washing clothes when the water is hard?
What is a detergent? Name one detergent.
Why have detergents replaced soap as a washing agent?
Explain the cleansing action of soap. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
A student takes 4 mL of distilled water in each of four test tubes I, II, III and IV, and then dissolves an equal amount of four different salts namely NaCl in I, CaCl2 in II, MgCl2 in III and KCl in IV. He then adds 8 drops of the given soap solution to each test tube and shakes the contents of the test tube 10 times. In which test tubes will enough lather (foam) be formed ?
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) I and IV
(D) III and IV
What are detergents chemically? List two merits and two demerits of using detergents for cleansing. State the reason for the suitability of detergents for washing, event in the case of water having calcium and magnesium ions.
Explain the action of soap in removing an oily spot from a piece of cloth.
Give a scientific explanation.
Soap forms a precipitate in hard water.
What is the difference between soaps and detergents? State, in brief, the cleansing action of soaps in removing an oily spot from a fabric. Why are soaps not very effective when a fabric is washed in hard water? How is this problem resolved?
What is meant by 'surface activity'?
Soaps were originally made from ______.
______ are substances which can undergo chemical changes to produce certain materials.
Why do soaps not work effectively in hard water?
