Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe in brief the cleansing action of soap.
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
उत्तर १
Cleansing action of soaps:
The dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and is insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by only washing with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water and, thus, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.

उत्तर २
The cleaning action of soap can be described as follows:
- A soap molecule has a tadpole-shaped structure.
- At one end (long, non-polar end) of the soap molecule is a hydrocarbon chain which is insoluble in water but soluble in oil.
- At the other end (short polar end) of the soap molecule, there is a carboxylate ion which is hydrophilic, i.e. water soluble but insoluble in oil.
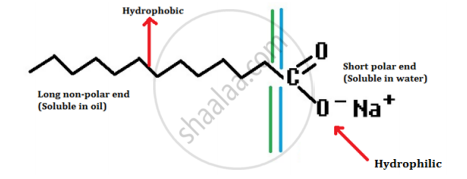
- Soap, on mixed with water, forms a concentrated solution and causes foaming.
- The long non-polar end of soap gravitates towards and surrounds the dirt and absorbs the dust in it.
- The short polar end with the carboxylate ion repels the water away from the dirt.
- A spherical aggregate of soap molecules is formed in the soap solution in water and is called a micelle.
- Thus, the soap molecule dissolves the dirt and our clothes get clean.
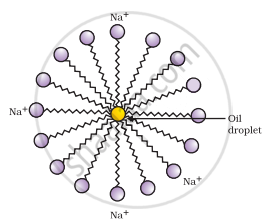
Formation of micelles
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Both soap and detergent are some type of salts. What is the difference between them?
While preparing soap a small quantity of common salt is generally added to the reaction mixture of vegetable oil and sodium hydroxide. Which one of the following may be the purpose of adding common salt?
(A) To reduce the basic nature of the soap
(B) To make the soap neutral
(C) To enhance the cleansing power of the soap
(D) To favour the precipitation of the soap
While studying the saponification reaction, what do you observe when you mix an equal amount of colourless vegetable oil and 20% aqueous solution of NaOH in a beaker?
(A) The colour of the mixture has become dark brown
(B) A brisk effervescence is taking place in the beaker
(C) The outer surface of the beaker has become hot
(D) The outer surface of the beaker has become cold
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
............. is better than soap for washing clothes when the water is hard.
What change will you observe if you test soap solution with a litmus paper (red and blue)? Give reason for your observation.
Why is common salt (sodium chloride) added during the preparation of soap?
Why have detergents replaced soap as a washing agent?
Describe the structure of a soap molecule with the help of a diagram.
The soap molecule has a ______.
Give the reason of formation of scum when soaps are used with hard water.
A student takes 4 mL of distilled water in each of four test tubes I, II, III and IV, and then dissolves an equal amount of four different salts namely NaCl in I, CaCl2 in II, MgCl2 in III and KCl in IV. He then adds 8 drops of the given soap solution to each test tube and shakes the contents of the test tube 10 times. In which test tubes will enough lather (foam) be formed ?
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) I and IV
(D) III and IV
Give a scientific explanation.
Soap forms a precipitate in hard water.
Differentiate between:
Detergents and Soaps.
Answer the following question.
In three test tubes A, B, and C, three different liquids namely, distilled water, underground water and distilled water in which a pinch of calcium sulphate is dissolved, respectively are taken. Equal amount of soap Answer is added to each test tube and the contents are shaken. In which test tube will the length of the foam (lather) be longest? Justify your answer.
Explain why soap cannot be used in hard water.
The saponification of a fat or oil is done using _____ solution for hot process.
Match the following
| 1. | Soap | C6H5 OH |
| 2. | Cement | CaSO4.2H2O |
| 3. | Fertilizers | NaOH |
| 4. | Gypsum | RCC |
| 5. | Phenol | NPK |
Soaps are ester of which type of acids?
______ are substances which can undergo chemical changes to produce certain materials.
