Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe in brief the cleansing action of soap.
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
उत्तर १
Cleansing action of soaps:
The dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and is insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by only washing with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water and, thus, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.

उत्तर २
The cleaning action of soap can be described as follows:
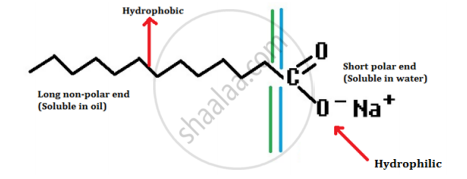
- A soap molecule has a tadpole-shaped structure.
- At one end (long, non-polar end) of the soap molecule is a hydrocarbon chain which is insoluble in water but soluble in oil.
- At the other end (short polar end) of the soap molecule, there is a carboxylate ion which is hydrophilic, i.e. water soluble but insoluble in oil.
- Soap, on mixed with water, forms a concentrated solution and causes foaming.
- The long non-polar end of soap gravitates towards and surrounds the dirt and absorbs the dust in it.
- The short polar end with the carboxylate ion repels the water away from the dirt.
- A spherical aggregate of soap molecules is formed in the soap solution in water and is called a micelle.
- Thus, the soap molecule dissolves the dirt and our clothes get clean.
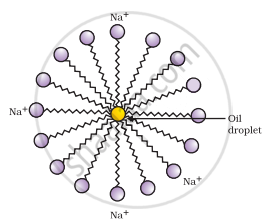
Formation of micelles
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why do soaps not form lather in hard water?
People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
A student took four test tubes P, Q, R and S and filled about 8 mL of distilled water in each. After that he dissolved an equal amount of Na2SO4 in P, K2SO4 in Q, CaSO4 in R and MgSO4 in S. On adding an equal amount of soap solution and shaking each test tube well, a good amount of lather will be obtained in the test tubes:
(a) P and Q
(b) P and R
(c) P, Q and S
(d) Q, R and S
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
............. is better than soap for washing clothes when the water is hard.
What change will you observe if you test soap solution with a litmus paper (red and blue)? Give reason for your observation.
Why have detergents replaced soap as a washing agent?
Which of the two is better for washing clothes when the water is hard: soap or detergent? Give reason for your answer.
Explain the cleansing action of soap. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
Which one of the following sets of materials can be used to prepare soap?
(A) Neem oil and calcium hydroxide
(B) Castor oil and sodium hydroxide
(C) Mineral oil and sodium hydroxide
(D) Neem oil and magnesium hydroxide
Give the reason of formation of scum when soaps are used with hard water.
A student is testing water to know which is best for cleansing purposes with soaps. He would find that the cleansing action of soaps is best when he uses water obtained from
(a) rain
(b) tap
(c) hand pump
(d) pond
What is meant by 'surface activity'?
What are the differences between Soap and synthetic detergent?
What are the differences between Bath soap and soap for washing clothes?
Explain why often coloured spots are formed on clothes during washing.
The saponification of a fat or oil is done using _____ solution for hot process.
In the soap micelles
What are soaps?
