Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
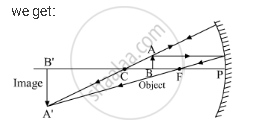
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays:
Solution
Using the following rules for image formation:
- A ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror is reflected along the same path, and
- A ray of light passing through the focus of a concave mirror becomes parallel to the principal axis after reflection,
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
With the help of an appropriate ray diagram, state the sign conventions for reflection by a spherical mirror.
"A concave mirror of focal length 15 cm can form a magnified, erect as well as inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror in both the cases for obtaining the images.
An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focused image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror making an angle of 90° with the mirror surface. The angle of reflection for this ray of light will be:
(a) 45°
(b) 90°
(c) 0°
(d) 60°
A concave mirror produces three times enlarged virtual image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror.
Which of the following are concave mirrors and which convex mirrors?
Shaving mirrors, Car headlight mirror, Searchlight mirror, Driving mirror, Dentist's inspection mirror, Touch mirror, Staircase mirror in a double-decker bus, Make-up mirror, Solar furnace mirror, Satellite TV dish, Shop security mirror.
If the image formed is always virtual, the mirror can be:
(a) concave or convex
(b) concave or plane
(c) convex or plane
(d) only convex
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between the focus and centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
A student has to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of angle of incidence.
(a) Write two important precautions for this experiment.
(b) List two conclusions the student will draw based on his experiment.
For a real object, which of the following can produce a real image?
