Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
With the help of an appropriate ray diagram, state the sign conventions for reflection by a spherical mirror.
Solution
The sign convention for reflection by spherical mirrors is as follows:-
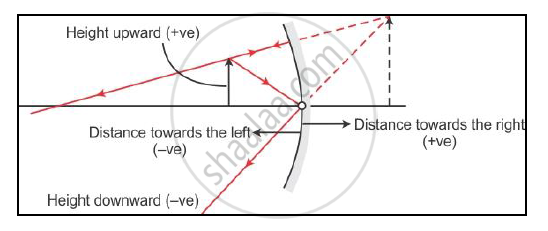
- The object is always placed to the left of the mirror.
- All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the pole of the mirror.
- All the distances measured to the right of the origin are taken as positive, while those measured to the left of the origin are taken as negative.
- Distances measured perpendicular to and above the principal axis are taken as positive.
- Distances measured perpendicular to and below the principal axis are taken as negative.
- The focal length of a convex mirror is positive, while that of a concave mirror is negative.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object of height 5 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 10 cm. If the distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens is 20 cm, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed using the lens formula.
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
List four specific characteristics of the images of the objects formed by convex mirrors.
To construct ray diagrams, two rays of light are generally so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from a mirror. Choose two such rays and state the path/direction of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the position and nature of the image of an object placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification −1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror:
(i) Write the type of mirror.
(ii) What is the nature of the image formed?
(iii) How far is the object located from the mirror?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
Three students A, B and C focussed a distant building on a screen with the help of a concave mirror. To determine focal length of the concave mirror they measured the distances as given below:
Student A : From mirror to the screen
Student B : From building to the screen
Student C : From building to the mirror
Who measured the focal length correctly ;
(a) Only A
(b) Only B
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
Which type of mirror is used by a dentist?
Define (i) principal focus of a concave mirror, and (ii) focal length of a concave mirror.
Draw diagram to represent the action of a concave mirror on a beam of parallel light rays. Mark on this diagram principal axis, focus F, centre of curvature C, pole P and focal length f, of the concave mirror.
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image of the object AB with the help of suitable rays:
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image with the help of suitable rays:
Explain why, a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected back along the same path.
With the help of a labelled ray diagram, describe how a converging mirror can be used to give an enlarged upright image of an object.
Explain why, concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors.
The real image formed by a concave mirror is smaller than the object if the object is:
(a) between centre of curvature and focus
(b) at a distance greater than radius of curvature
(c) at a distance equal to radius of curvature
(d) at a distance equal to focal length
What is the position of the image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
At what distance from a concave mirror focal length 10 cm should an object 2 cm long be placed in order to get an erect image 6 cm tall?
When an object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror, its image is formed at 10 cm in front of the mirror. Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
A man holds a spherical shaving mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, and focal length 30 cm, at a distance of 15 cm, from his nose. Find the position of image, and calculate the magnification.
An object is placed just outside the principal focus of concave mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and describe its size, position and nature.
A concave mirror cannot be used as:
(a) a magnifying mirror
(b) a torch reflector
(c) a dentist's mirror
(d) a real view mirror
The mirror which can form a magnified image of an object is:
(a) convex mirror
(b) plane mirror
(c) concave mirror
(d) both convex and concave mirror
Draw and complete the following diagrams to show what happens to the beams of light as they enter the glass block and then leave it:
Name the lens which can concentrate sun's rays to a point and burn a hole in a piece of paper.
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain how a concave lens diverges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the concave lens on the diagram.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object placed beyond the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
State two uses of a concave mirror.
In the following diagram. MM' is a concave mirror and AB is an object. Draw on your answer-sheet a ray diagram to show the formation of image of this object.
A student has to determine the focal length of a concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object on a screen. For getting best result he should focus
(A) a distant tree or an electric pole
(B) a well-illuminated distant building
(C) well-lit grills of the nearest window
(D) a burning candle laced at the distant edge of the laboratory table
Draw the ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
Answer the following question:
An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use the lens formula to determine the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) in this case.
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram to justify your answer of the part (ii)
Match the following.
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parobolic mirror | Rear – view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
Large ______ mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnaces.
Concave mirrors are used by dentists to examine teeth. Why?
A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
The image formed by concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object. The position of object should be ______.
Define principal focus of the concave mirror.
