Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw and complete the following diagrams to show what happens to the beams of light as they enter the glass block and then leave it:
Solution
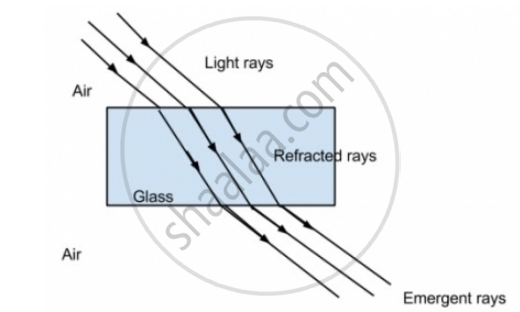
When a beam of light rays enters the glass block, it gets refracted. It bends towards the normal. Also, when these light rays leave the block, they bend away from the normal.
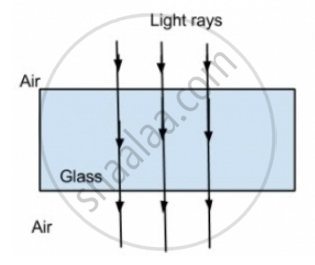
When light rays fall normally on the surface of the glass block, there is no bending of rays; the rays travel straight.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror and show the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.
An object of size 7.0 cm is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 18 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed, so that a sharp focused image can be obtained? Find the size and the nature of the image.
An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image.
Draw the following diagram in your answer book and show the formation of image with the help of suitable rays:
State where an object must be placed so that the image formed by a concave mirror is:
(b) at infinity.
(c) the same size as the object.
Name the type of mirror used by dentists. How does it help?
A large concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 1.5 m. A person stands 10 m in front of the mirror. Where is the person's image?
Draw the ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at the centre of curvature of the mirror.
Name the mirror(s) that can give (i) an erect and enlarged image, (ii) same sized, inverted image
The ENT doctor uses a ______.
