Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is ............. its focal length.
Solution
Radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is two times its focal length
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
"A concave mirror of focal length 15 cm can form a magnified, erect as well as inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror in both the cases for obtaining the images.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror.
Explain why, a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror gets reflected back along the same path.
Which type of mirror is used in a solar furnace? Support your answer with reason.
How can a concave mirror be used to obtain a virtual image of an object? Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Match the following.
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parobolic mirror | Rear – view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
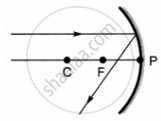
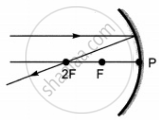
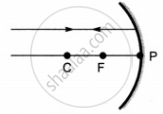
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?

 |
 |
 |
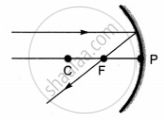 |
| A | B | C | D |
A concave mirror of radius 30 cm is placed in water. It’s focal length in air and water differ by ______.
The image formed by concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object. The position of object should be ______.
In torches, searchlights, and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed ______ of the concave mirror.
