Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe an experiment to show that a light ray bends when it passes from one transparent medium into another transparent medium.
Solution 1
EXPERIMENT: Spread and fix a sheet of white paper on the drawing board.
At the centre of the paper, place a glass slab XYX ‘Y’ and draw its boundary.
A ray of light AB travelling from air (rarer medium) to glass slab (denser medium). Part of path BC in denser medium bends towards the normal.
∠r ∠i. This shows that when light travels from RARER to DENSER medium bends towards the normal. Ray BC travels from DENSER medium to RARER medium in air (RAY CD) bend away from normal. ∠e >∠r.
This shows that when a ray of light travels from DENSER to RARER medium bends AWAY from normal.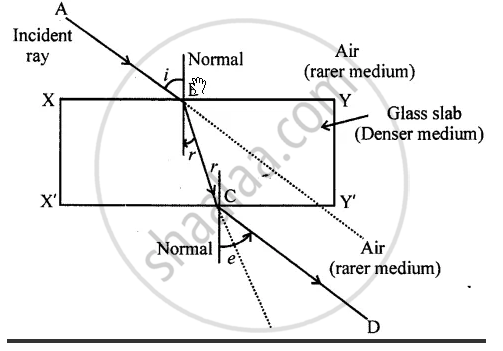
Solution 2
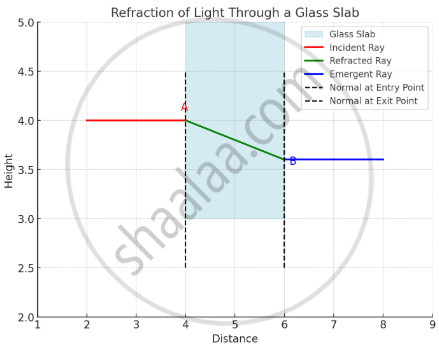
To demonstrate that a light ray bends (refracts) when it passes from one transparent medium into another.
Procedure:
-
Set Up the Experiment: Place the white paper on a flat surface. Put the glass slab on the paper and trace its outline with a pencil.
-
Draw the Incident Ray: Draw a straight line approaching one side of the glass slab at an angle (not perpendicular). Mark the point where the incident ray meets the glass slab as A.
-
Shine the Light: Direct the laser pointer or ray box along the incident ray towards A.
-
Observe the Refracted Ray: On the other side of the glass slab, observe the path of the light as it emerges. Mark the exit point as B.
-
Trace the Path: Remove the glass slab and use a ruler to draw the refracted ray inside the slab and the emergent ray outside.
-
Measure Angles: Measure the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at point A.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The angle between the normal and refracted ray is called
Name the mirror which forms an erect, virtual and enlarged image of an object. What is the position of object relative to the mirror?
What is a real image? Name the mirror which can be used to obtain the real image of an object. What should be the position of the object relative to the mirror?
The image formed by a pinhole camera is inverted because,
Figure shows a pencil placed above a mirror
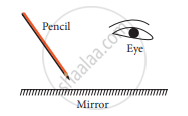
- Draw its image formed by the mirror
- Show how light rays from the object are reflected at the mirror to form the image for the eye.
We can create enlarged, virtual images with ______.
The image which can be obtained on a screen is called ______.
Magnification for the ______ image is always ______.
A real image is inverted and can be caught on the screen.
Distinguish between real & virtual images.
