Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
between its pole and focus
Describe the nature, size and position of the image formed in each case.
State one use of concave mirror bases on the formation of image as in case (i) above.
Solution
When an object is placed between the centre of curvature and the focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is real, inverted, and enlarged. This is illustrated as follows:

Here, the image A'B' of the object AB, placed between the centre of curvature and the focus of a concave mirror, is real and inverted.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
To determine the approximate value of the focal length of a given concave mirror, you focus the image of a distant object formed by the mirror on a screen. The image obtained on the serene, as compared to the object is always:
(a) Laterally inverted and diminished
(b) Inverted and diminished
(c) Erect and diminished
(d) Erect and highly diminished
Draw diagram to represent the action of a concave mirror on a beam of parallel light rays. Mark on this diagram principal axis, focus F, centre of curvature C, pole P and focal length f, of the concave mirror.
An object is placed just outside the principal focus of concave mirror. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and describe its size, position and nature.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed between the pole and focus of a concave mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image.
How can a concave mirror be used to obtain a virtual image of an object? Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
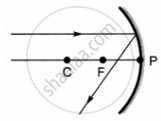
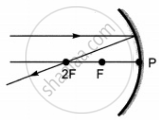
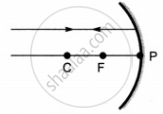
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in figure?

 |
 |
 |
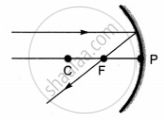 |
| A | B | C | D |
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image larger than the actual object?
The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object, the position of the object should be ______.
Write the uses of the concave mirror.
