Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Give two circumstances in which a concave mirror can form a magnified image of an object placed in front of it. Illustrate your answer by drawing labelled ray diagrams for both.
Solution
The two circumstances in which a concave mirror can form a magnified image of an object that is placed in front of it are:
- When an object is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is virtual, erect and magnified, as shown in the figure. Here, the object AB is placed between the pole and the focus of a concave mirror. Its image A'B' is formed behind the
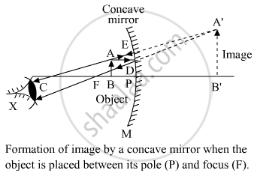
mirror and is virtual, erect and magnified.
- When an object is placed between the centre of curvature and the focus of a concave mirror, the image formed is real, inverted and enlarged, as shown in figure 2. Here, the object AB is placed between the centre of curvature and the focus of a concave mirror. Its image A'B' is formed beyond the centre of curvature and is real, inverted and enlarged.

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Describe the New Cartesian Sigh Convention used in optics. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate this sign convention.
When an object is placed 20 cm from a concave mirror, a real image magnified three times is formed. Find:
(a) the focal length of the mirror.
(b) Where must the object be placed to give a virtual images three times the height of the object?
Write down the magnification formula for a lens in terms of object distance and image distance. How does this magnification formula for a lens differ from the corresponding formula for a mirror?
What is the nature of the image formed by a convex lens if the magnification produced by the lens is +3?
An object is placed at a distance of 100 cm from a converging lens of focal length 40 cm.
(i) What is the nature of image?
(ii) What is the position of image?
Magnification produced by a concave lens is always:
(a) more than 1
(b) equal to 1
(c) less than 1
(d) more than 1 or less than 1
In order to obtain a magnification of, –3 (minus 3) with a convex lens, the object should be placed:
(a) between optical centre and F
(b) between F and 2F
(c) at 2F
(d) beyond 2F
In order to obtain a magnification of, –0.75 with a convex lens of focal length 8 cm, the object should be placed:
(a) at less than 8 cm
(b) between 8 cm and 16 cm
(c) beyond 16 cm
(d) at 16 cma
A convex mirror has a focal length of 18 cm. The image of an object kept in front of the mirror is half the height of the object. What is the distance of the object from the mirror?
What do you mean by linear magnification?
