Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1.0 on a screen placed at a distance of 30 cm from the pole of the mirror.
(i) Write the type of mirror in this case.
(ii) What is the focal length of the mirror ?
(iii) What is the nature of the image formed ?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Solution
Given :
m=-1 , v=-30 cm
We know that,
`m=-v/u`
`therefore -1=(30)/u`
`therefore u=-30`
(i) Since the magnification has a negative sign, the typa of mirror is a concave mirror
(ii) Using `1/f=1/v+1/u`, we get
`1/f=-1/30+(-1)/30`
`therefore 1/f=-2/30`
`therefore1/f=-1/15`
`=>f=-15` cm
∴ Focal length of the concave mirror is 15 cm
(iii) Since the magnitude of magnification is equal to 1 and the sign of magnification is negative, the image will be of the same size as the object, and its nature will be real and inverted.
(iv)
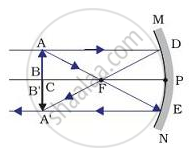
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
"A concave mirror of focal length 15 cm can form a magnified, erect as well as inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror in both the cases for obtaining the images.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases:-
A ray of light incident on a concave lens is
(i) passing through its optical centre.
(ii) parallel to its principal axis.
(iii) directed towards its principal focus.
A communications satellite in orbit sends a parallel beam of signals down to earth. If these signals obey the same laws of reflection as light and are to be focussed onto a small receiving aerial, what should be the best shape of the metal 'dish' used to collect them?
Which type of mirror is used in a solar furnace? Support your answer with reason.
Name the type of mirror used by dentists. How does it help?
An object is 24 cm away from a concave mirror and its image is 16 cm from the mirror. Find the focal length and radius of curvature of the mirror, and the magnification of the image.
To construct ray diagram we use two light rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List these two rays and state the path of these rays after reflection. Use these rays to locate the image of an object placed between centre of curvature and focus of a concave mirror.
A student has to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of angle of incidence.
(a) Write two important precautions for this experiment.
(b) List two conclusions the student will draw based on his experiment.
According to cartesion sign convention, which mirror and which lens has negative focal length?
