Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why are concave mirrors used in solar devices?
Solution
A concave mirror is also known as a converging mirror because of its ability to focus parallel rays of light at a single point on its focal plane. This property is used in solar devices. Parallel rays from the Sun, when reflected by the concave mirror, are focused at a particular point, generating a significant amount of heat. This heat is essential for the proper functioning of solar devices, such as solar cookers or solar furnaces.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer. Where and why do we generally use this type of mirror?
Consider the following diagram in which M is a mirror and P is an object and Q is its magnified image formed by the mirror.
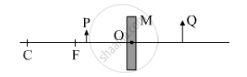
State the type of the mirror M and one characteristic property of the image Q.
A student obtained a sharp image of a candle flame placed at the distant end of the laboratory table on a screen using a concave mirror to determine its focal length. The teacher suggested him to focus a distant building, about 1 km away from the laboratory, for getting more correct value of the focal length. In order to focus the distant building on the same screen, the student should slightly move the
(a) mirror away from the screen
(b) screen away from the mirror
(c) screen towards the mirror
(d) screen towards the building
Study the following diagram and select the correct statement about the device 'X' :

(A) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of radius of curvature 12 cm
(B) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 6 cm
(C) Device 'X' is a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm
(D) Device 'X' is a convex of mirror of focal length 12 cm
Name the type of mirror used in the following situation:
Headlights of a car
Support your answer with reason.
Which type of mirror is used by a dentist?
With the help of a ray diagram, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
Give two uses of concave mirrors. Explain why you would choose concave mirrors for these uses.
The image formed by a concave mirror is real, inverted and highly diminished (much smaller than the object). The object must be:
(a) between pole and focus
(b) at focus
(c) at the centre of curvature
(d) at infinity
Write down a formula for the magnification produced by a concave mirror.
in terms of height of object and height of image
An object 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror which produces a virtual image 4.5 cm high:
(i) What is the focal length of the mirror?
(ii) What is the position of image?
(iii) Draw a ray-diagram to show the formation of image.
A concave mirror produces three times enlarged virtual image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Calculate the radius of curvature of the mirror.
If the object is moved further away from the mirror, what changes are there in the position and size of the image?
What type of mirror should be used as a shaving mirror?
A real image of an object is to be obtained. The mirror required for this purpose is:
(a) convex
(b) concave
(c) plane
(d) either convex or concave
Why does a beam of light when it enters glass at an angle? Why does it not bend if it inters the glass at right angles?
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
A concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed ______.
A concave mirror of focal length 20 cm forms an image having twice the size of object. For the virtual position of object, the position of object will be at ______.
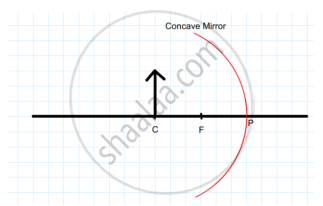
Examine the above figure and state which of the following option is correct? [one small box in the figure is equal to 1 cm]
