Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
Solution
We know that:
(i) When an object is beyond the 2F point of a convex lens, the image formed by it is real, inverted, and diminished in size.
(ii) When the object is in between the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of the convex lens, the image formed by it is real, inverted, and enlarged.
(iii) When the object is between the ‘F’ point and the optical centre of the convex lens, the image formed by it is virtual, erect, and enlarged.
We thus notice that there is a sudden change in the nature of the image formed when an object approaching from infinity, crosses the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens. It is for this reason that we regard these two points as a sort of turning point as far as the nature of the image formed by a convex lens is concerned.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its real, inverted and magnified image?
If an object is at a considerable distance (or infinity) in front of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a real magnified image by a convex lens. (In your sketch the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus of lens should be shown clearly).
An object 50 cm tall is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens. Its 20 cm tall image is formed on the screen placed at a distance of 10 cm from the lens. Calculate the focal length of the lens.
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted magnified image?
Study the diagram below.
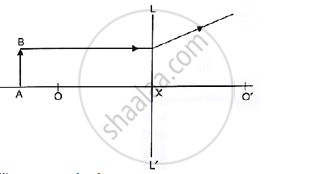
what are the points O, O’ called?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is of the same size as the object?
Observe the following figure and answer the questions.
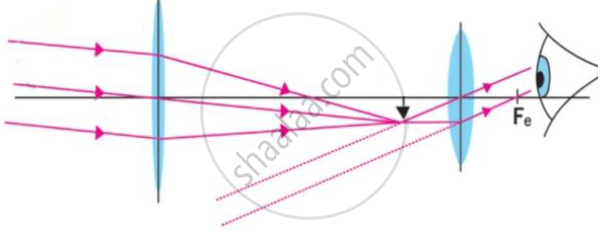
a) Which optical instrument shows arrangement of lenses as shown in the figure?
b) Write in brief the working of this optical instrument.
c) How can we get different magnifications in this optical instrument?
d) Draw the figure again and labelled it properly
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : _______
