Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
Solution
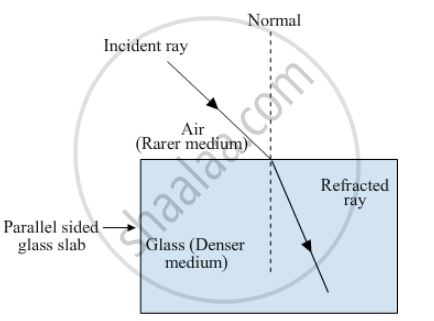
When a ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel side glass slab, it bends towards the normal.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A student has obtained a magnified image of a flame on a screen using a convex lens. To draw the corresponding ray diagram to show the image formation, which of the following two rays whose paths after refraction are shown, should he select ?
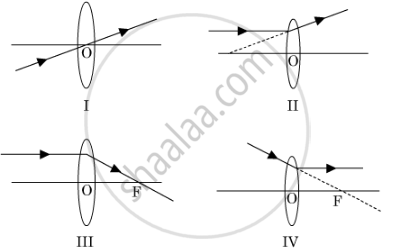
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) III and IV
(D) I and III
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

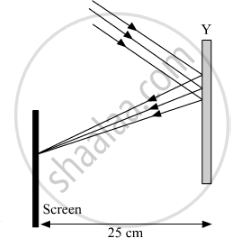
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
When a ray of light enters from one medium to another having different optical densities it bends. Why does this phenomenon occur?
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The image in a convex lens depends upon the distance of the ........... from the lens.
Define principal axis, principal focus and focal length of a convex lens.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a real magnified image by a convex lens. (In your sketch the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus of lens should be shown clearly).
How could you find the focal length of a convex lens rapidly but approximately?
A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. At which of the following position should an object be placed so that this convex lens may act as a magnifying glass?
(a) 15 cm
(b) 7 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 25 cm
The image obtained while finding the focal length of convex lens is ....................
