Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How could you find the focal length of a convex lens rapidly but approximately?
Solution
To determine the focal length of a convex lens, place the convex lens in a holder and keep it in front of a distant object like a tree. A cardboard screen is put behind the lens. Now, change the distance of the screen from the convex lens until a clear, inverted image of the tree is formed on the screen. Measure the distance of the screen from the lens. This distance will be the focal length of the convex lens. Here, we have used the fact that the image of an object at a far distance is formed at the focus of a convex lens.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
One-half of a convex lens is covered with a black paper. Will this lens produce a complete image of the object? Verify your answer experimentally. Explain your observations.
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

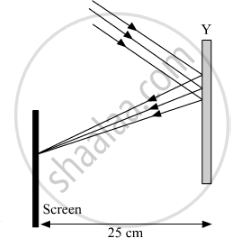
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the formation of image of a finite object placed in front of convex lens between f and 2f. Give two characteristics of the image so formed.
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
Which causes more bending (or more refraction) of light rays passing through it : a convex lens of long focal length or a convex lens of short focal length?
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as in searchlight.
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
