Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
Solution
d1 = 5 cm = 50 mm
m = `"v"/"u" = "d"_2/"d"_1`
`66.6/-200 = "d"_2/50`
d2 = 16.65 mm = 1.66 cm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The diagram given alongside shows a ray of light entering a rectangular block of glass.
(a) Copy the diagram and draw the normal at the point of entry.
(b) Draw the approximate path of the ray of light through the glass block and out of the other side.
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted diminished image?
Which part causes the greatest convergence?
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. Draw a diagram to illustrate it.
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.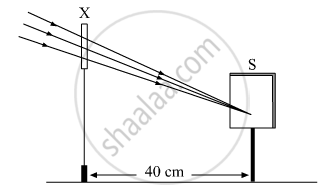
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
Observe the following figure and complete the table:

| Points | Answer |
| (i) Position of the object | |
| (ii) Position of the image | |
| (iii) Size of the image | |
| (iv) Nature of the image |
State the nature and position of the object on the principal axis to obtain a real image of the same size
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
