Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
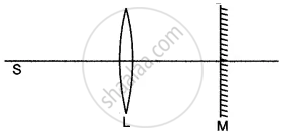
Solution
The complete ray diagram is shown below:
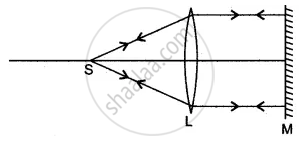
The point S is called the focus of the lens.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity (considerable distance) in front of a convex lens. State three characteristics of the image so formed.
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What would be the image distance if the object distance was 90 cm?
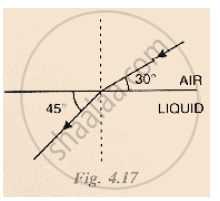
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from sir to a liquid.
(a) write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) use snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
Study the diagram given below.
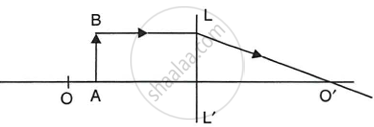
- Name the lens LL’.
- What are the points O and O’ called?
- Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
- State the three characteristics of the image.
- Name a device in which this action of lens is used.
Complete the following table:
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| Convex | Between optical centre and focus | ||
| Convex | At focus | ||
| Concave | At infinity | ||
| Concave | At any distance |
Draw a diagram to show the convergent action of a convex lens by treating it as a combination of glass block and two triangular glass prisms, with the aid of two parallel incident rays.
Can one bum a piece of paper in daylight by just using a convex lens instead of a match or any direct flame? Support your answer with the help of an appropriate ray diagram.
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : _______
