Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
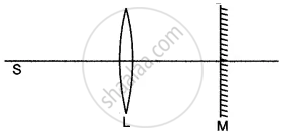
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
उत्तर
The complete ray diagram is shown below:
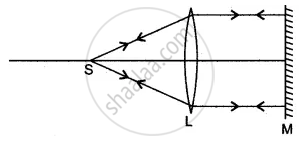
The point S is called the focus of the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
f the image formed by a convex lens is of the same size as that of the object, what is the position of the image with respect to the lens?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its real, inverted and magnified image?
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
An object 4 cm high is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

Where is the image formed?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is at infinity?
Out of the two lenses one concave and the other convex state which is a convergent or a divergent type of a lens. Give a reason for your answer.
