Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
उत्तर
Given:
Size of object, h = 2 cm
Focal length, f = 5 cm
Object distance, u =-10 m =-1000 cm
Applying lens formula, we get:
1/v - 1/u = 1/f
1/v = 1/f + 1/u
or, 1/v = 1/5 + 1/(-1000)
or, 1/v=(-200+1)/-1000
or, 1/v=199/1000
or, 1/v=1000/199
or, v=5 cm (approx)
Image distance, v =5 cm behind the lens;
Applying magnification formula, we get:
m = h'/h = v/u
m = h'/2 = (5)/(-1000)
or, h' =-0.01 cm
Thus, the size of the image is 0.01 cm.
So, the image is inverted (h' is negative), highly diminished (h' is smaller than h) and real (v is positive).
Therefore, from the above results we conclude that:
When an object is placed beyond 2f, the image is real, inverted and diminished and is formed between f and 2f.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student focuses the image of a well-illuminated distant object on a screen using a convex lens. After that, he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen by adjusting the lens.
(i) In which direction, towards the screen or away from the screen, does he move the lens?
(ii) What happens to the size of the image? Does it decrease or increase?
(iii) What happens to the image on the screen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
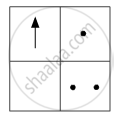
(a)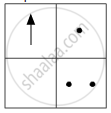
(b)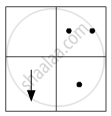
(c)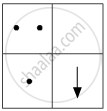
(d)
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations:
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –60 | +12 |
| 2 | –30 | +15 |
| 3 | –20 | +20 |
| 4 | –15 | +30 |
| 5 | –12 | +60 |
| 6 | –9 | +90 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? State reason for your answer.
(b) For what object-distance (u) is the corresponding image-distance (v) not correct? How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Choose an appropriate scale to draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
If you are to determine to focal length of a convex lens, you should have
(A) a convex lens and a screen
(B) a convex lens and a lens holder
(C) a lens holder, a screen holder and a scale
(D) a convex lens, a screen, holder for them and a scale
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of photographic camera.
Diagram shows an object AB placed on the principal axis B of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens.
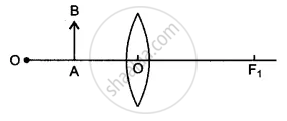
(i) Copy the diagram:
Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens. Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens. Locate the final image
(ii) Is the image real or virtual?
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
