Advertisements
Advertisements
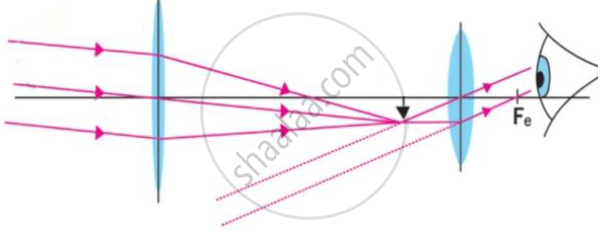
प्रश्न
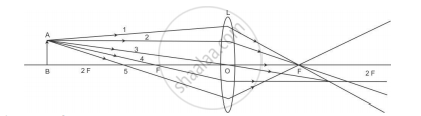
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
उत्तर
- The above type of lens construction is used in a compound microscope.
- The image formed by the objective is real, inverted, and formed at a distance within the focal length of the eyepiece.
- If the object is placed in between O and Fo, a virtual image will be formed on the same side of the objective as that of the object. As a result, compound microscope will not be able to operate as expected.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
"A convex lens can form a magnified erect as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Draw ray diagram to justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the lens in each case.
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
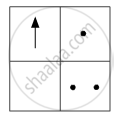
(a)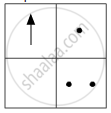
(b)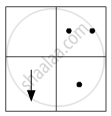
(c)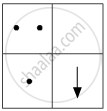
(d)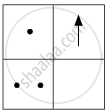
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

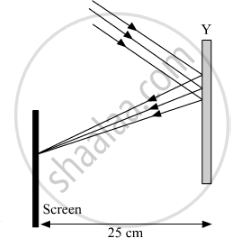
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from an optically denser medium into air.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its real, inverted and magnified image?
What type of lens would you use as a magnifying glass? How close must the object be to the lens?
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity (considerable distance) in front of a convex lens. State three characteristics of the image so formed.
With the help of a labelled diagram explain how a convex lens converges a beam of parallel light rays. Mark the principal axis, optical centre, principal focus and focal length of the convex lens on the diagram.
A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. At which of the following position should an object be placed so that this convex lens may act as a magnifying glass?
(a) 15 cm
(b) 7 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 25 cm
A convex lens of focal length 8 cm forms a real image of the same size as the object. The distance between object and its image will be:
(a) 8 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 24 cm
(d) 32 cm
Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.50 m
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
A convex lens of focal length 10 cm is placed in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. The focal length of this combination of lenses will be:
(a) +10 cm
(b) +20 cm
(c) −10 cm
(d) −20 cm
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Name the type of lens.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is at infinity?
State two applications of a convex lens.
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.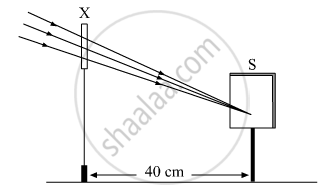
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
For finding the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object, one should use as the object.
(1) a well lit distant tree
(2) window grill in the class room
(3) any distant tree
(4) a lighted candle kept at the other end of the table.
Observe the following figure and answer the questions.
a) Which optical instrument shows arrangement of lenses as shown in the figure?
b) Write in brief the working of this optical instrument.
c) How can we get different magnifications in this optical instrument?
d) Draw the figure again and labelled it properly
Yesh find out F1 and F2 of symmetric convex lens experimentally then which conclusion is true.
Draw neat diagram to show the
Convergent action of a convex lens,
(a) What type of a lens can be used as a magnifying glass?
(b) Show by a ray diagram the formation of a real image by simple magnifying lens.
Where must a point source of light be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain a parallel beam of light?
Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the determination of the focal length of a convex lens using an auxiliary plane mirror.
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : _______
Write scientific reason.
Adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
Differentiate convex lens and concave lens.
Which of the following statements is true?
Which of the following statements is true?
A convex lens of focal length 20 cm can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
