Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
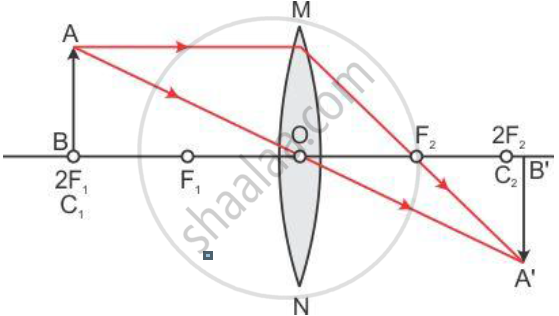
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image of an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens
उत्तर
The ray diagram:-
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
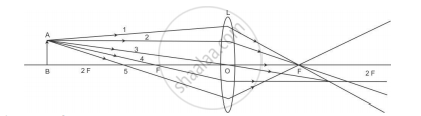
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
An object of height 2.5 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical 'O', principal focus F and height of the image on the diagram.
Complete the following table:
| Instrument | Number of Convex Lenses |
Use |
| Simple Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Compound Microscope | .............. | .............. |
| Telescope | .............. | .............. |
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity (considerable distance) in front of a convex lens. State three characteristics of the image so formed.
What type of lens is used to correct
hypermetropia
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
How will you decide whether a given piece of glass is a concave lens, convex lens, or a plane glass plate?
In sunglasses, both of its surfaces are curved, yet their behaviour is neither like a convex lens nor like a concave lens. State the reason.
Define the terms principal foci and focal lengths as applied to a convex lens, and show them with the help of proper diagrams.
Which of the following statements is true?
