Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
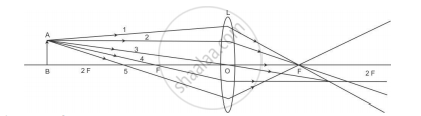
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
उत्तर
(D) 2, 3 and 4
Ray 2, 3 and 4 are obeying the laws of refraction.
Ray 2 is parallel to the principal axis and passes through the principal focus after refraction.
Ray 3 passes from the optical centre of the lens and emerges without any deviation.
Ray 4 is passing through the principal focus and after refraction from a convex lens emerges parallel to the principal axis.
Ray 1 and 5 cannot pass through the focus after refraction as they are not parallel to the principal axis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
The image in a convex lens depends upon the distance of the ........... from the lens.
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Rewrite the image distances in the correct order.
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a convex lens. Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through the lens.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is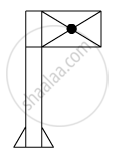
(A)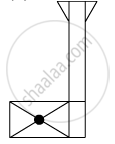
(B)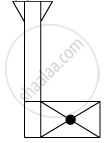
(C)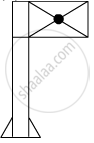
(D)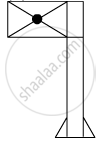
A student places a 8.0 cm tall object perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. He obtains a sharp image of the object on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. What will be the nature (inverted, erect, magnified, diminished) of the image he obtains on a screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
Yesh find out F1 and F2 of symmetric convex lens experimentally then which conclusion is true.
What happens to the image formed by a convex lens if its lower part is blackened?
