Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 10 cm to study the image formation by a convex lens for the various positions of the object. In one of his observations, he may observe that when the object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from the lens, its image is formed at (select the correct option)
(A) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, real and erect.
(B) 40 cm on the other side of the lens and is magnified, real and inverted.
(C) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, real and inverted.
(D) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, virtual and erect.
उत्तर १
(C) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, real and inverted.
Focal length f = 10 cm
The object is placed at 2F (2 ⨯ 10 = 20 cm). Hence the image is also formed at 2F.
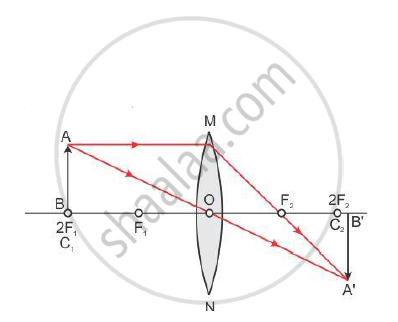
| Position of object | Position of image | Size of image | Nature of image |
| At 2F1 | At 2F2 | Same size | Real and inverted |
उत्तर २
Focal length of the lens, f = 10 cm
Object distance, u = −20 cm (negative sign is used due to sign convention)
Using the lens formula:
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
`rArr1/10=1/v-1/(-20)`
`rArr1/v=1/10-1/20`
`rArr1/v=(2-1)/20`
`rArrv=20" cm"`
Hence, the image will be formed on the other side of the lens.
Magnification is given as:
`m=v/u=h_i/h_o`
`h_i/h_o=20/(-20)`
`h_i=-h_o`
Therefore, the image formed by the convex lens will be of same size, real and inverted.
Hence, the correct option is C.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A divergent lens of focal length 30 cm forms the image of an object of size 6 cm on the same side as the object at a distance of 15 cm from its optical centre. Use lens formula to determine the distance of the object from the lens and the size of the image formed.
If a magnification of, −1 (minus one) is to be obtained by using a converging mirror, then the object has to be placed:
(a) between pole and focus
(b) at the centre of curvature
(c) beyond the centre of curvature
(d) at infinity
In order to obtain a magnification of, −0.6 (minus 0.6) with a concave mirror, the object must be placed:
(a) at the focus
(b) between pole and focus
(c) between focus and centre of curvature
(d) beyond the centre of curvature
Linear magnification (m) produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles:
(a) is equal to one
(b) is less than one
(c) is more than one
(d) can be more less than one depending on the position of object
To determine focal length of a concave mirror a student obtains the image of a well lit distant object on a screen. To determine the focal length of the given concave mirror he needs to measure the distance between:
(A) mirror and the object
(B) mirror and the screen
(C) screen and the object
(D) screen and the object and also mirror and the screen
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance 36 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed at a distance of 72 cm from the lens. Identify the type of lens and calculate its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.5 cm, find the height of its image.
An object is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 20 cm.
- Find the position of the image, and
- the magnification of the image.
The image of a candle flame formed by a lens is obtained on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. If the image is three times the size of the flame and the distance between lens and image is 80 cm, at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens? What is the nature of the image at a distance of 80 cm and the lens?
Ravi kept a book at a distance of 10 cm from the eyes of his friend Hari. Hari is not able to read anything written in the book. Give reasons for this?
The focal length of a concave lens is 20 cm. At what distance from the lens should a 5 cm tall object be placed so that its image is formed at a distance of 15 cm from the lens? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
