Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 10 cm to study the image formation by a convex lens for the various positions of the object. In one of his observations, he may observe that when the object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from the lens, its image is formed at (select the correct option)
(A) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, real and erect.
(B) 40 cm on the other side of the lens and is magnified, real and inverted.
(C) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, real and inverted.
(D) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, virtual and erect.
Solution 1
(C) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, real and inverted.
Focal length f = 10 cm
The object is placed at 2F (2 ⨯ 10 = 20 cm). Hence the image is also formed at 2F.
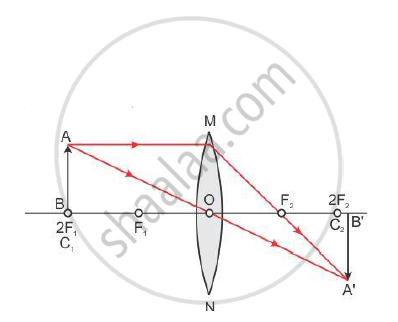
| Position of object | Position of image | Size of image | Nature of image |
| At 2F1 | At 2F2 | Same size | Real and inverted |
Solution 2
Focal length of the lens, f = 10 cm
Object distance, u = −20 cm (negative sign is used due to sign convention)
Using the lens formula:
`1/f=1/v-1/u`
`rArr1/10=1/v-1/(-20)`
`rArr1/v=1/10-1/20`
`rArr1/v=(2-1)/20`
`rArrv=20" cm"`
Hence, the image will be formed on the other side of the lens.
Magnification is given as:
`m=v/u=h_i/h_o`
`h_i/h_o=20/(-20)`
`h_i=-h_o`
Therefore, the image formed by the convex lens will be of same size, real and inverted.
Hence, the correct option is C.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When an object is placed at a distance of 50 cm from a concave spherical mirror, the magnification produced is, `-1/2`. Where should the object be placed to get a magnification of, `-1/5`?
Magnification produced by a convex mirror is always:
(a) more than 1
(b) less than 1
(c) equal to 1
(d) more or less than 1
Draw a diagram to show how a converging lens held close to the eye acts as a magnifying glass. Why is it usual to choose a lens of short focal length for this purpose rather than one of long focal length?
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual magnified image of an object by a convex lens. In your diagram, the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus should be shown clearly.
The lens A produces a magnification of, − 0.6 whereas lens B produces a magnification of + 0.6.
What is the nature of lens B?
Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens is used as a magnifying glass to observe a small object. Mark on your diagram the foci of the lens and the position of the eye.
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 80 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the candle flame at a distance of 20 cm from its pole.
- Which type of mirror should the student use?
- Find the magnification of the image produced.
- Find the distance between the object and its image.
- Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case and mark the distance between the object and its image.
To determine focal length of a concave mirror a student obtains the image of a well lit distant object on a screen. To determine the focal length of the given concave mirror he needs to measure the distance between:
(A) mirror and the object
(B) mirror and the screen
(C) screen and the object
(D) screen and the object and also mirror and the screen
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance 15 cm from it, at a distance 60 cm in front of it. Find the magnification.
Write an expression for magnification for a lens, explaining the meaning of the symbols used.
