English Medium
Academic Year: 2013-2014
Date: March 2014
Advertisements
The atomic numbers of three elements A, B and C are 12, 18 and 20 respectively. State, giving reason, which two elements will show similar properties.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population. Why?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Write one negative effect of affluent lifestyle of few persons on the environment.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
Draw labelled diagrams to illustrate budding in Hydra.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
"A concave mirror of focal length 15 cm can form a magnified, erect as well as inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror in both the cases for obtaining the images.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
State with reason any two possible consequences of elimination of decomposers from the Earth.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
What is water harvesting?
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
How can water harvesting technique help in the conservation of water?
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
Study the following table in which positions of six elements A, B, C, D, E and F are shown as they are in the modern periodic table:
|
Group→
Period↓ |
1
|
2
|
3-12
|
13
|
14
|
15
|
16
|
17
|
18
|
| 2 | A | B | C | ||||||
| 3 | D | E | F |
On the basis of the above table, answer the following questions:-
(i) Name the element which forms only covalent compounds.
(ii) Name the element which is a metal with valency three.
(iii) Name the element which is a non-metal with valency three.
(iv) Out of D and E, which is bigger in size and why?
(v) Write the common name for the family to which the elements C and F belong.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
The elements Be, Mg and Ca each having two electrons in their outermost shells are in periods 2, 3, and 4 respectively of the modern periodic table. Answer the following questions, giving justification in each case:-
(i) Write the group to which these elements belong.
(ii) Name the least reactive element.
(iii) Name the element having largest atomic radius.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
A carboxylic acid (molecular formula C2H4O2) reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst to form a compound 'X'. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidification gives the same carboxylic acid C2H4O2. Write the name and structure of
(i) carboxylic acid, (ii) alcohol and (iii) the compound 'X'.
Chapter:
Define the term ‘structural’ isomerism'.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Explain why propane cannot exhibit the structural isomerism property.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Draw the structures of possible isomers of butane, C4H10.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 90 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the flame at a distance of 15 cm from its pole.
(a) Suggest the type of mirror he should use.
(b) Determine the linear magnification in this case.
(c) Find the distance between the object and its image.
(d) Draw ray diagram to show the image formation in this case
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of the refracted ray in each of the following cases:-
A ray of light incident on a concave lens is
(i) passing through its optical centre.
(ii) parallel to its principal axis.
(iii) directed towards its principal focus.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A narrow beam PQ of white light is passing through a glass prism ABC as shown in the diagram.
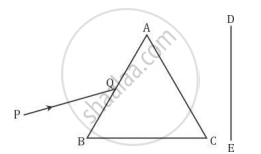
Trace it on your answer sheet and show the path of the emergent beam as observed on the screen DE.
(i) Write the name and cause of the phenomenon observed.
(ii) Where else in nature is this phenomenon observed?
(iii) Based on this observation, state the conclusion which can be drawn about the constituents of white light.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Advertisements
"Energy flow in a food chain is unidirectional" Justify this statement.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Explain how the pesticides enter a food chain and subsequently get into our body.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
Write one difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Which species is likely to have better chances of survival - the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Justify your answer.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
What is the effect of DNA copying, which is not perfectly accurate, on the reproduction process? How does the amount of DNA remain constant though each new generation is a combination of DNA copies of two individuals?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
List three main factors responsible for the speciation and briefly describe each one of them
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
"A trait may be inherited, but may not be expressed." Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
List two reasons for carbon forming a large number of compounds. Name the type of bonding found in most of its compounds. Why does carbon form compounds mainly by this kind of bonding?
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Give reason why the carbon compounds generally have low melting and boiling points.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Give reason why the carbon compounds do not conduct electricity in the molten state.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
List the parts of the human eye that control the amount of light entering into it. Explain how they perform this function.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Write the function of retina in human eye.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Do you know that the corneal-impairment can be cured by replacing the defective cornea with the cornea of the donated eye? How and why should we organise groups to motivate the community members to donate their eyes after death?
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- optical centre
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- centres of curvature
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal axis
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- aperture
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses:- principal focus
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Explain the following term related to spherical lenses: focal length
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A converging lens has focal length of 12 cm. Calculate at what distance the object should be placed from the lens so that it forms an image at 48 cm on the other side of the lens.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Draw a sectional view of human female reproductive system and label the part where
(i) eggs develop.
(ii) fertilisation takes place.
(iii) fertilised egg gets implanted.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Describe, in brief, the changes the uterus undergoes
(i) to receive the zygote.
(ii) if zygote is not formed
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Name the parts labelled as A, B, C and D in the diagram given below:-
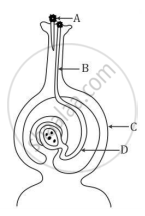
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Answer the following question.
What is pollination? Explain the different types of pollination.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
How does fertilisation occur in flowers? Name the parts of the flower that develop into (i) seed, and (ii) fruit after fertilisation.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Answer the following question.
State significance of pollination.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
In the following diagram showing the structure of embryo of a dicot seed, what are the parts marked I, II and III sequentially?
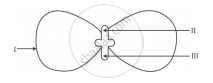
Plumule, Cotyledon, Radicle
Plumule, Radicle, Cotyledon
Cotyledon, Plumule, Radicle
Radicle, Plumule, Cotyledon
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Study the following statements:-
I. Wings of birds and wings of bats are homologous organs.
II. Wings of birds and wings of insects are modified forelimbs.
III. Wings of birds and wings of insects are analogous organs.
IV. Wings of birds and forelimbs of horse are homologous organs.
The correct statements are
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) III and IV
(D) I and IV
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Advertisements
Which of the following pairs of two vegetables represent the correct homologous structures?
(A) Sweet potato and potato
(B) Sweet potato and tomato
(C) Carrot and potato
(D) Radish and carrot
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
When you study a slide showing different stages of budding in yeast, you observe the following stages:-
I. The bud may get separated from the parent body and develop into a new individual.
II. The body of the bud develops and gives rise to another baby bud.
III. A bud comes out in any direction from the body of the parent cell.
IV. Thus they may form a colony.
The proper sequence of the above stages is
(A) II, I, III, IV
(B) II, III, I, IV
(C) III, II, l, IV
(D) III, I, II, IV
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A student has to focus his compound microscope to observe a prepared slide showing different stages of binary fission in Amoeba. The steps he is likely to follow are listed below in a haphazard manner:
I. Adjust the diaphragm and the mirror of the microscope so that sufficient light may enter to illuminate the slide.
II. Fix the slide on the stage carefully.
III. Adjust the microscope to high power and focus.
IV. Adjust the microscope to low power and focus.
The correct sequence of the above steps to observe the slide under the microscope is
(A) I, II, IV, III
(B) II, I, IV, III
(C) II, IV, I, III
(D) I, IV, II, III
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A student takes about 2 mL ethanoic acid in a dry test tube and adds a pinch of sodium hydrogen carbonate to it. He reports the following observations:
I. Immediately a colourless and odourless gas evolves with a brisk effervescence.
II. The gas turns lime water milky when passed through it.
III. The gas burns with an explosion when a burning splinter is brought near it.
IV. The gas extinguishes the burning splinter that is brought near it.
The correct observations are
(A) I, II and III
(B) II, III and IV
(C) III, IV and I
(D) I, II and IV
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
In an experiment to study the properties of ethanoic acid, a student takes about 3 mL of ethanoic acid in a dry test tube. He adds an equal amount of distilled water to it and shakes the test tube well. After some time he is likely to observe that
(A) a colloid is formed in the test tube.
(B) the ethanoic acid dissolves readily in water.
(C) the solution becomes light orange.
(D) water floats over the surface of ethanoic acid.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
We need 20% aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide for the study of saponification reaction. When we open the lid of the bottle containing solid sodium hydroxide we observe it in which form?
(A) Colourless transparent beads
(B) Small white beads
(C) White pellets/flakes
(D) Fine white powder
Chapter: [0.02] Acids, Bases and Salts
While studying saponification reaction, a student measures the temperature of the reaction mixture and also finds its nature using blue/red litmus paper. On the basis of his observations the correct conclusion would be
(A) the reaction is exothermic and the reaction mixture is acidic.
(B) the reaction is endothermic and the reaction mixture is acidic.
(C) the reaction is endothermic and the reaction mixture is basic.
(D) the reaction is exothermic and the reaction mixture is basic.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
In a locality, hard water, required for an experiment, is not available. However, the following salts are available in the school laboratory:
1. Sodium sulphate
2. Calcium sulphate
3. Magnesium chloride
4. Sodium chloride
5. Calcium chloride
6. Potassium sulphate
Which of the above salts may be dissolved in water to obtain hard water for the experiment?
(A) 2, 3 and 5
(B) 1, 2 and 5
(C) 1, 2, 4 and 6
(D) 3 and 5 only
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student focused the Sun rays using an optical device 'X' on a screen S as shown.

From this it may be concluded that the device 'X' is a (select the correct option)
(A) Convex lens of focal length 10 cm.
(B) Convex lens of radius of curvature 20 cm.
(C) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(D) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student has obtained an image of a well-illuminated distant object on a screen to determine the focal length, F1of the given spherical mirror. The teacher then gave him another mirror of focal length, F2 and asked him to obtain a focused image of the same object on the same screen. The student found that in order to focus the same object using the second mirror, he has to move the mirror away from the screen. From this observation, it may be concluded that both the spherical mirrors given to the student were (select the correct option)
(A) Concave and F1 < F2
(B) Concave and F1 > F2
(C) Convex and F1 < F2
(D) Convex and F1 > F2
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
In the following diagram, the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism is shown:
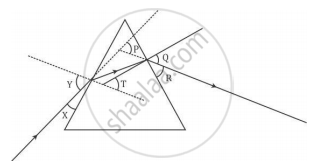
In this diagram the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the angle of deviation respectively are (select the correct option):
(A) X, R and T
(B) Y, Q and T
(C) X, Q and P
(D) Y, Q and P
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Study the following diagrams in which the path of a ray of light passing through a glass prism as traced by four students P, Q, R and S is shown:
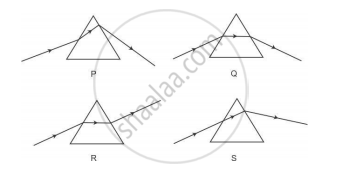
The student who has traced the path correctly is
(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
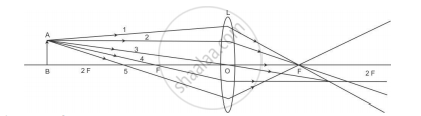
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 10 cm to study the image formation by a convex lens for the various positions of the object. In one of his observations, he may observe that when the object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from the lens, its image is formed at (select the correct option)
(A) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, real and erect.
(B) 40 cm on the other side of the lens and is magnified, real and inverted.
(C) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, real and inverted.
(D) 20 cm on the other side of the lens and is of the same size, virtual and erect.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab and marks the angle of incidence i, angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e, as shown.
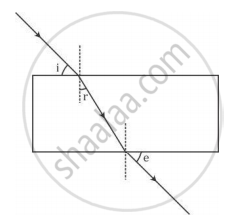
The correctly marked angle(s) is/are
(A) ∠ i only
(B) ∠ e only
(C) ∠ r only
(D) ∠ i and ∠ e
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
After tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of the angle of incidence, a student reported his observations in tabular form as given below:
| S.No | ∠ i | ∠ r | ∠ e |
| I | 30° | 19° | 29° |
| II | 40° | 28° | 40° |
| III | 50° | 36° | 50° |
| IV | 60° | 40° | 59° |
The best observation is
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2013 - 2014
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2014 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
