Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Answer the following question.
What is pollination? Explain the different types of pollination.
What is meant by pollination?
Solution 1
The transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is known as pollination.
It is of two types:-
- Self-pollination:-It is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant.
- Cross-pollination:-It is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the flower present on two different plants.
Solution 2
Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the flower.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Stigma | (a) Neuron |
| (ii) Pepsin | (b) Carpel |
| (iii) Dendrites | (c) Protein |
| (d) Stamen |
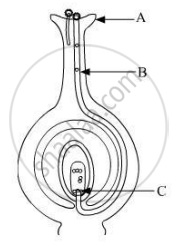
Name the parts A, B and C shown in the diagram and write their functions.
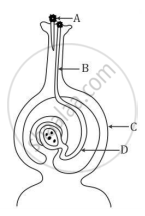
Name the parts labelled as A, B, C and D in the diagram given below:-
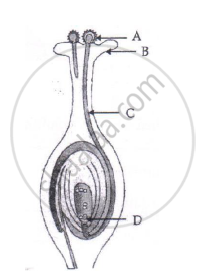
(i) Name the part marked 'A' in the diagram.
(ii) How dose 'A' reachese part 'B'?
(iii) State the importance of the part 'C'.
(iv) What happens to the part marked 'D' after fertilisation is over?
State the function of flowers in the flowering plants.
The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as ______.
Name the part made up of the stigma, style and ovary.
Name the swollen lower part of the carpel.
What is the function of a flower?
What is the name of female organ of a flower (other than carpel)?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The ovule becomes a .......... after fertilisation.
Explain the terms 'cross-pollination'?
What type of plants reproduce by sexual reproduction method?
What is seed? What are the parts of a seed? Explain with the help of a labelled diagram.
In tobacco plant, the male gametes have 24 chromosomes.
What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete?
What is meant by 'unisexual flowers' and 'bisexual flowers'? Give two examples of each.
In the figure given alongside, the parts marked A, B and C are sequentially :
(a) cotyledon, plumule and radicle
(b) plumule, radicle and cotyledon
(c) plumule, cotyledon and radicle
(d) radicle, cotyledon and plumule
In what ways is fertilisation in a plant similar to fertilisation in a human?
Fill in the blank by selecting suitable word:
A flower that bears both the male and the female parts is known as __________ flower.
Multiple choice question. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
Unisexual flowers are found in
- mulberry
- mustard
- pea
- sunflower
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F):
Stamens make egg cells.
What are the male and female gametes in a flowering plant?
Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival – the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reason to justify your answer.
Give one example each of unisexual and bisexual flowers. Differentiate between the two types of pollination that occur in flowers. What happens when a pollen lands on a suitable stigma? Write about the events that occur till the seed formation in the ovary.
Draw a diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth into the ovule and label the following:
Pollen grain, male gamete, female gamete, ovary.
Distinguish between unisexual and bisexual flowers giving one example of each. Draw a diagram showing process of germination of pollen grains on stigma and label the following parts:
(a) Female germ cell
(b) Male germ cell
(c) Ovary
Fill in the blank by selecting suitable word:
Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as______________.
What is pollination? Mention its types.
Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower and label the following parts.
Give scientific reason.
Flower is a structural unit of sexual reproduction in plants.
Distinguish between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Explain the sexual reproduction process in plants with a diagram.
Write the events involved in the sexual reproduction of a flowering plant.
Discuss the first event and write the types.
Which of the following is the outermost protective layer of anther?
How many middle layers are generally present in the wall of the anther lobes?
Which type of development is observed in male gametophytes of plants?
The 3-celled egg apparatus at the micropylar end comprises of ______
Gloriosa superba exhibits ______.
In a flowering plant, archesporium gives rise to ______.
Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
- They possess both stamen and pistil
- They possess either stamen or pistil
- They exhibit cross pollination
- Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
Is the chromosome number of zygote, embryonal cells and adult of a particular organism always constant? How is the constancy maintained in these three stages?
Trace the path a male gamete takes to fertilise a female gamete after being released from the penis.
State the number of sets of chromosomes present in a zygote.
Double fertilization means ______.
What is the structural unit of sexual reproduction in plant?
Sexual maturation of reproductive tissues and organs are necessary link for reproduction. Elucidate.
In flowering plants, the pollen grains are transferred to stigma by pollination but the female germ cells are present in the ovary.
Explain with the help of a labelled diagram (only concerned parts), how the male germ cell reaches the ovary.
