Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
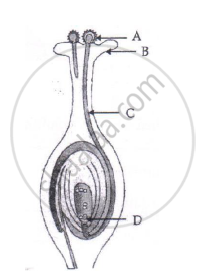
(i) Name the part marked 'A' in the diagram.
(ii) How dose 'A' reachese part 'B'?
(iii) State the importance of the part 'C'.
(iv) What happens to the part marked 'D' after fertilisation is over?
Solution
(i) Part ‘A’ labelled is pollen grain.
(ii) Part ‘B’ is stigma. The pollen grain reaches the stigma during pollination.
(iii) Part ‘C’ is the pollen tube. The pollen tube carries the gametes to the embryo sac for fertilisation.
(iv) Part ‘D’ is the egg cell. After fertilisation with the male gametes, the egg cell forms the zygote.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Sketch the reproductive parts of a flower.
State the name of the functional unit concerned with sexual reproduction.
Where is the male gamete formed in flowering plants?
The flask-shaped organ A at the centre of a flower is surrounded by a number of little stalks B having swollen tops which lie just inside the ring of petals.
(a) Name A. What are the various parts of A?
(b) Which part of A contains gametes?
(c) Name B. What is the swollen top of B known as?
(d) What does the swollen top of b contain?
(e) Out of A and B, which one is (i) male part, and (ii) female part of the flower?
Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statement
Pollen is produced in the:
Multiple choice question. Tick (✓) the correct choice:
The male gamete is present inside the which germinates.
- the style
- the stigma
- the anther
- the ovary
Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival – the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reason to justify your answer.
Distinguish between unisexual and bisexual flowers giving one example of each. Draw a diagram showing process of germination of pollen grains on stigma and label the following parts:
(a) Female germ cell
(b) Male germ cell
(c) Ovary
What are the agents for pollination?
Triple fusion involves ______.
