Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
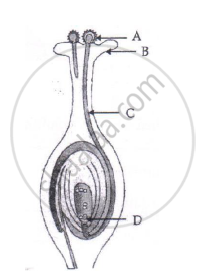
(i) Name the part marked 'A' in the diagram.
(ii) How dose 'A' reachese part 'B'?
(iii) State the importance of the part 'C'.
(iv) What happens to the part marked 'D' after fertilisation is over?
उत्तर
(i) Part ‘A’ labelled is pollen grain.
(ii) Part ‘B’ is stigma. The pollen grain reaches the stigma during pollination.
(iii) Part ‘C’ is the pollen tube. The pollen tube carries the gametes to the embryo sac for fertilisation.
(iv) Part ‘D’ is the egg cell. After fertilisation with the male gametes, the egg cell forms the zygote.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The female organ of reproduction in the flower is the...........
What is seed? What are the parts of a seed? Explain with the help of a labelled diagram.
Explain the process of fertilisation in flowers.
A student is asked to study the different parts of an embryo of pea seeds. Given below are the essential steps for the experiment :
(I) Soak the pea seeds in plain water and keep them overnight.
(II) Cut open the soaked seed and observe its different parts.
(III) Take some pea seeds in a petri dish.
(IV) Drain the excess water. Cover the seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them as it is for a day.
The correct sequence of these steps is
(A) III, I, IV, II
(B) III, IV, I, II
(C) III, I, II, IV
(D) III, II, I, IV
List any two differences between pollination and fertilisation.
Pollen grains from anther are transferred to the stigma.
Antipodal cells are present towards the ______ in an anatropous ovule.
Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
- They possess both stamen and pistil
- They possess either stamen or pistil
- They exhibit cross pollination
- Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
Type of sexual reproduction is ______.
State the post-fertilisation changes that lead to fruit formation in plants.
