English Medium
Academic Year: 2015-2016
Date & Time: 2nd March 2016, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
Write the name and structure of an aldehyde with four carbon atoms in its molecule.
Chapter:
List two functions ovary of human female reproductive system.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
In a food chain of frog, grass, insect and snake, assign trophic level to frog.
Chapter: [0.13] Our Environment
The refractive indices of glass and water with respect to air are 3/2 and 4/3 respectively. If speed of light in glass is 2 x 108 m/s, find the speed of light in water.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
List four stakeholders which may be helpful in the conservation of forests.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
The construction of large dams leads to social and environmental problems. List two problems of each category.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
The position of eight elements in the Modern Periodic Table is given below where atomic numbers of elements are given in the parenthesis.
| Period No. | ||
| 2 | Li(3) | Be(4) |
| 3 | Na(11) | Mg(12) |
| 4 | K(19) | Ca(20) |
| 5 | Rb(37) | Sr(38) |
(i) Write the electronic configuration of Ca.
(ii) Predict the number of valence electrons in Rb.
(iii) What is the number of shells in Sr?
(iv) Predict whether K is a metal or a non – metal.
(v) Which one of these elements has the largest atom in size?
(vi) Arrange Be, Ca, Mg and Rb in the increasing order of the size of their respective atoms.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
Write three different chemical reactions showing the conversion of ethanoic acid to sodium ethanoate. Write balanced chemical equation in each case. Write the name of the reactants and the products other ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate in each case.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
An element 'X' belong to 3rd period and group 13 of the Modern Periodic Table.
(a) Determine the valence electrons and the valency of 'X'.
(b) Molecular formula of the compound formed when 'X' reacts with an element 'Y' (atomic number = 8).
(c) Write the name and formula of the compound formed when 'X' combines with chlorine
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
An element 'X' has mass number 35 and number of neutrons 18. Write atomic number and electronic configuration of 'X'. Also write group number, period number and valency of 'X'.
Chapter: [0.05] Periodic Classification of Elements
List two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce? [0.08] Heredity
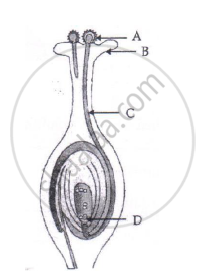
(i) Name the part marked 'A' in the diagram.
(ii) How dose 'A' reachese part 'B'?
(iii) State the importance of the part 'C'.
(iv) What happens to the part marked 'D' after fertilisation is over?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Advertisements
Define reproduction.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Explain the term “Regeneration” as used in relation to reproduction of organisms
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Describe briefly how regeneration is carried out in multicellular organisms like Hydra.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
“Two areas of study namely 'evolution' and 'classification' are interlinked'. Justify this statement.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
How do Mendel's experiment show that traits are inherited independently?
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
The activities of man had adverse effects on all forms of living organisms in the biosphere. Unlimited exploitation of nature by man disturbed the delicate ecological balance between the living and non-living components of the biosphere. The unfavourable conditions created by man himself threatened the survival not only of himself but also of the entire living organisms on the mother earth. One of your classmates is an active member of 'Eco club' of your school which is creating environmental awareness amongst the school students, spreading the same in the society and also working hard for preventing environmental degradation of the surroundings
Why is it necessary to conserve our environment?
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
The activities of man had adverse effects on all forms of living organisms in the biosphere. Unlimited exploitation of nature by man disturbed the delicate ecological balance between the living and non-living components of the biosphere. The unfavourable conditions created by man himself threatened the survival not only of himself but also of the entire living organisms on the mother earth. One of your classmates is an active member of 'Eco club' of your school which is creating environmental awareness amongst the school students, spreading the same in the society and also working hard for preventing environmental degradation of the surroundings.
State the importance of green and blue dust-bins in the safe disposal of the household waste
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
The activities of man had adverse effects on all forms of living organisms in the biosphere. Unlimited exploitation of nature by man disturbed the delicate ecological balance between the living and non-living components of the biosphere. The unfavourable conditions created by man himself threatened the survival not only of himself but also of the entire living organisms on the mother earth. One of your classmates is an active member of 'Eco club' of your school which is creating environmental awareness amongst the school students, spreading the same in the society and also working hard for preventing environmental degradation of the surroundings
List two values exhibited by your classmate who is an active member of Eco-club of your school.
Chapter: [0.16] Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
The image formed by a spherical mirror is real, inverted and is of magnification -2. If the image is at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror, where is the object placed? Find the focal length of the mirror. List two characteristics of the image formed if the object is moved 10 cm towards the mirror.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Describe an activity to show that colours of white light splitted by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light by another identical glass prism. Also draw ray diagram to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
What should be the range of distance of an object placed in front of the mirror?
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Where will the image of this object be, if it is placed 24 cm in front of the mirror? Draw ray diagram for this situation also justify your answer. Show the positions of pole, principal focus and the centre of curvature in the above ray diagrams
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Define evolution. How does it occur?
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
Describe how fossils provide us evidences in support of evolution.
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
What is placenta?
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
Describe placenta structure.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
State its functions in case of a pregnant human female.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
A carbon compound 'P' on heating with excess conc. H2SO4 forms another carbon compound 'Q' which on addition of hydrogen in the presence of nickel catalyst forms a saturated carbon compound 'R'. One molecule of 'R' on combustion forms two molecules of carbon dioxide and three molecules of water. Identify P, Q and R and write chemical equations for the reactions involved
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
What is atmospheric refraction? Use this phenomenon to explain the following natural events:
Twinkling of stars
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answers.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
What is atmospheric refraction? Use this phenomenon to explain the following natural events:
Advanced sun-rise and delayed sun-set.
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answers.
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Advertisements
Define focal length of a divergent lens.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A divergent lens of focal length 30 cm forms the image of an object of size 6 cm on the same side as the object at a distance of 15 cm from its optical centre. Use lens formula to determine the distance of the object from the lens and the size of the image formed.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image in the above situation
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student while observing an embryo of a pea seed in the laboratory listed various parts of the embryo as given below:
Testa, Tegmen, Radicle, Plumule, Micropyle, Cotyledon.
On examining the list the teacher remarked that only three parts are correct. Select three correct parts from the above list:
(a) Testa, Radicle, Cotyleddon
(b) Tegmen, Radicle, Micropyle
(c) Cotyledon, Plumule, Testa
(d) Radicle, Cotyledon, Plumule
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
If you are asked to select a group of two vegetables, out of the following, having homologous structures which one would you select?
(a) Carrot and radish
(b) Potato and sweet potato
(c) Potato and tomato
(d) Lady finger and potato
Chapter: [0.08] Heredity
In the following ray diagram the correctly marked angle are:
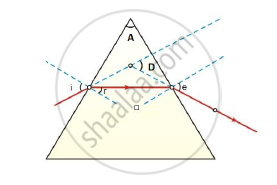
(a) ∠i and ∠e
(b) ∠A and ∠D
(c) ∠i, ∠e and ∠D
(d) ∠r, ∠A and ∠D
Chapter: [0.1] The Human Eye and the Colourful World
In your laboratory you trace the path of light rays through a glass slab for different values of angle of incidence (∠i) and in each case measure the values of the corresponding angle of refraction (∠r) and angle of emergence (∠e). On the basis of your observations your correct conclusion is:
(a) ∠i is more than ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(b) ∠i is less then ∠r, but nearly equal to ∠e
(c) ∠i is more than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
(d) ∠i is less than ∠e, but nearly equal to ∠r
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
To determine the approximate value of the focal length of a given concave mirror, you focus the image of a distant object formed by the mirror on a screen. The image obtained on the serene, as compared to the object is always:
(a) Laterally inverted and diminished
(b) Inverted and diminished
(c) Erect and diminished
(d) Erect and highly diminished
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
Suppose you have focused on a screen the image of candle flame placed at the farthest end of the laboratory table using a convex lens. If your teacher suggests you to focus the parallel rays of the sun, reaching your laboratory table, on the same screen, what you are expected to do is to move the:
(a) lens slightly towards the screen
(b) lens slightly away from the screen
(c) lens slightly towards the sun
(d) lens and screen both towards the sun
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
For preparing soap in the laboratory we require an oil and a base. Which of the following combinations of an oil and a base would be best suited for the preparation of soap?
(a) Castor oil and calcium hydroxide
(b) Turpentine oil and sodium hydroxide
(c) Castor oil and sodium hydroxide
(d) Mustard oil and calcium hydroxide
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student puts a drop of reaction mixture of a saponification reaction first a blue litmus paper and then on a red litmus paper. He may observe that:
(a) There is no change in the blue litmus paper and the red litmus paper turns white.
(b) There is no change in the red litmus paper and the blue litmus paper turns red.
(c) There is no change in the blue litmus paper and the red litmus paper turns blue.
(d) No change in colour is observed in both the litmus papers
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
In the neighbourhood of your school, hard water required for an experiment is not available. Select from the following group of salts available in your school, a group each member of which, if dissolved in distilled water, will make it hard:
(a) Sodium chloride, calcium chloride
(b) Potassium chloride, sodium chloride
(c) Sodium chloride, magnesium chloride
(d) Calcium chloride, magnesium chloride
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
A student is observing a permanent slide showing sequentially the different stages of asexual reproduction taking place in yeast. Name this process and draw diagrams, of what he observes, in a proper sequence.
Chapter: [0.07] How do Organisms Reproduce?
An object of height 2.5 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical 'O', principal focus F and height of the image on the diagram.
Chapter: [0.09] Light - Reflection and Refraction
A student adds a spoon full of powdered sodium hydrogen carbonate to a flask containing ethanoic acid. List two main observations, he must note in his note book, about the reaction that takes place. Also write chemical equation foe the reaction.
Chapter: [0.04] Carbon and its Compounds
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 10 Science with solutions 2015 - 2016
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 10 Science-2016 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Science, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 10.
How CBSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Science will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
