Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How do Mendel's experiment show that traits are inherited independently?
उत्तर १
Mendel carried out dihybrid crosses by crossing two pea plants differing in contrasting traits of two characters. For example, he crossed a pea plant having yellow colour and round seed characters with another pea plant bearing green colour and wrinkled seed characters. In the F2 generation, he obtained pea plants with two parental and two recombinant phenotypes as yellow round and green wrinkled (parental) and yellow wrinkled and green round (recombinant). This indicated that traits separated from their original parental combinations and got inherited independently.

उत्तर २
Mendel crossed pure-breeding tall plants with round seeds and pure-breeding short plants with wrinkled seeds. The plants of the F1 generation were all tall with round seeds, indicating that the traits of tallness and round seeds were dominant. Self-breeding of F1 yielded plants with characters of 9 tall round seeded, 3 tall wrinkled seeded, 3 short round seeded, and 1 short wrinkled seeded. Tall wrinkled seeded and short round seeded plants are new combinations which can develop only when the traits are inherited independently.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits – blood group A or O – is dominant? Why or why not?
What constitutes the link between one generation and the next?
Name the scientist who gave the laws of inheritance.
What sizes of plants are produced if both parents have genes Tt?
For his experiments on heredity, Mendel used :
papaya plants
potato plants
pea plants
pear plants
A pregnant woman has an equal chance of her baby being blood group A or blood group AB. Which one of the following shows the possible genotypes of the woman and the father of her child?
(a) IA IA and IB IO
(b) IA IB and IB IO
(c) IA IO and IB IO
(d) IA IB and IA IO
Pure-bred tall pea plants are first crossed with pure-bred dwarf pea plants. The pea plants obtained in F1generation are then cross-bred to produce F2 generation of pea plants.
(a) What do the plants of F1 generation look like?
(b) What is the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2 generation?
(c) Which type of plants were missing in F1 generation but reappeared in F2 generation?
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits-blood group A or O - is dominant? Why or why not?
Mendel first crossed pure-bred pea plants having round-yellow seeds with pure-bred pea plants having wrinkled-green seeds and found that only round-yellow seeds were produced in the F1 generation. When F1generation pea plants having round-yellow seeds were cross-bred by self pollination, then peas having round-yellow seeds, round green seeds, wrinkled-yellow seeds and wrinkled-green seeds were produced. Mendel collected a total of 2160 seeds.
(a) What will be the number of (i) round green seeds (ii) wrinkled green seeds (iii) round yellow seeds, and (iv) wrinkled-yellow seeds?
(b) Which 'ratio' as established by Mendel have you made use of in answering the part (a) above?
List two differences in tabular form between dominant trait and recessive traits. What percentage/proportion of the plants in the F2 generation/progeny were round, in Mendel's cross between round and wrinkled pea plants?
"It is possible that a trait is inherited but may not be expressed." Give a suitable example to justify this statement.
Explain Mendel’s law of independent inheritance. Give one example.
____________ refers to the transmission of genetic information from parental generation to next generation.
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes, what will be the colour of eyes of the persons having combinations
(i) Bb and (ii) BB?
If a tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant then, what percentage of F1 and F2 generation respectively will be tall?
In the following figure showing a germinating gram seed, name the parts labelled as A, B and C:
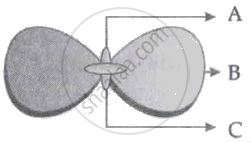
Why is Part 'B' considered to be important during germination?
A cross between pea plant with white flowers (vv) and pea plant with violet flowers (VV) resulted in F2 progeny in which ratio of violet (VV) and white (vv) flowers will be ______.
Mendel crossed pea plants with two pairs of contrasting characters.
| RRYY | × |
rryy |
| Round, Yellow | Wrinkled, Green |
He observed 4 types of combinations in F2 generation. Which of the combinations were new? Write the conclusion drawn by this experiment.
