Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write scientific reason.
Adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
उत्तर
- The ability of the ciliary muscles near the eye lens to change the focal length of the lens decreases with age.
- As a result, sometimes adults suffer from both nearsightedness and farsightedness.
Therefore, adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student focuses the image of a well-illuminated distant object on a screen using a convex lens. After that, he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen by adjusting the lens.
(i) In which direction, towards the screen or away from the screen, does he move the lens?
(ii) What happens to the size of the image? Does it decrease or increase?
(iii) What happens to the image on the screen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
"A convex lens can form a magnified erect as well as magnified inverted image of an object placed in front of it." Draw ray diagram to justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the lens in each case.
To find the image-distance for varying object-distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image of the screen.
(a) In which direction – towards or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image – does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on the walls of school laboratory by using a lens:-
(a) Which type of lens should be use and why?
(b) At what distance in terms of focal length 'F' of the lens should be place the candle flame so as to get (i) a magnified, and (ii) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
(c) Draw ray diagram to show the formation of the image in each case?
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
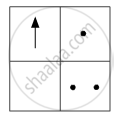
(a)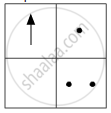
(b)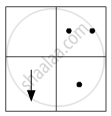
(c)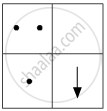
(d)
An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
A beam of light travelling in air is incident of water. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in water.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel sided glass block:
if it hits the glass block at 90° (that is, perpendicular to the glass block)
If an object is placed at the focus of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
What type of lens would you use as a magnifying glass? How close must the object be to the lens?
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a real magnified image by a convex lens. (In your sketch the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus of lens should be shown clearly).
An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f in front of a convex lens. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image. State two characteristics of the image formed.
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity (considerable distance) in front of a convex lens. State three characteristics of the image so formed.
List some things that convex lens and concave mirror have in common.
An object is placed f and 2f of a convex lens. Which of the following statements correctly describes its image?
(a) real, larger than the object
(b) erect, smaller than the object
(c) inverted, same size as object
(d) virtual, larger than the object
In order to obtain a real image twice the size of the object with a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, the object distance should be:
(a) more than 5 cm but less than 10 cm
(b) more than 10 cm but less than 15 cm
(c) more than 15 cm but less than 30 cm
(d) more than 30 cm but less than 60 cm
If the object is moved to a point only 3 cm away from the lens, what is the new position, height and nature of the image?
How would a pencil look like if you saw it through How would a pencil look like if you saw it through
A beam of parallel light rays is incident through the holes on one side of a box and emerges out through the holes on its opposite side as shown in the diagram below:
Which of the following could be inside the box?
(a) a rectangular glass block
(b) a concave lens
(c) a convex lens
(d) a glass prism
What kind of lens can form:
an inverted magnified image?
What kind of lens can form:
an erect magnified image?
An image formed on a screen is three times the size of the object. The object and screen are 80 cm apart when the image is sharply focussed.
State which type of lens is used.
What type of lens is used to correct
hypermetropia
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Name the type of lens.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. Draw a diagram to illustrate it.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. State two more characteristics of the image.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is of the same size as the object?
For finding the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object, one should use as the object.
(1) a well lit distant tree
(2) window grill in the class room
(3) any distant tree
(4) a lighted candle kept at the other end of the table.
Point out the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens.
How will you decide whether a given piece of glass is a concave lens, convex lens, or a plane glass plate?
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the determination of the focal length of a convex lens using an auxiliary plane mirror.
Can one bum a piece of paper in daylight by just using a convex lens instead of a match or any direct flame? Support your answer with the help of an appropriate ray diagram.
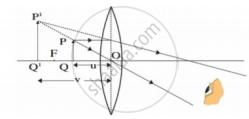 : Object near the lens : : ______ :
: Object near the lens : : ______ : 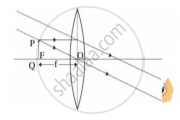
Differentiate convex lens and concave lens.
Which of the following statements is true?
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
