Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 7 - Lenses SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 7 - Lenses - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-and-technology-1-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Lenses
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of Maharashtra State Board SCERT Maharashtra for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Choose the correct option.
Choose the correct option.
A ray of light gets refracted ______ while entering the lens.
once
twice
thrice
doesn’t happen
The point inside the lens on the principal axis through which light rays pass without changing their path is called _______.
centre of curvature
optical centre
principal focus
axiom point
Virtual image is formed by a convex lens if an object is placed _______.
at infinity
at 2F1
at focus F1
between F1 and O
In the convex lens if an object is placed at 2 F1, the image is formed at ______.
F1
2 F2
beyond 2 F1
On the same side of the lens as the object
All distances parallel to the principal axis are measured from the _______.
optical centre
centre of curvature
principal focus
infinity
A small hole of changing diameter at the centre of Iris is called _______.
optic nerves
cornea
optic disc
pupil
For a normal human eye the near point is at _______.
2.1 cm
2.5 cm
25 cm
5 cm
The image formed by _______ lens is always virtual and small.
plane convex
biconvex
biconcave
bifocal
In a relaxed state, the focal length of healthy eyes is _______.
2 cm
2.5 cm
25 cm
5 cm
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
power 2 D; convex lens
power 1 D; concave lens
power - 0.5 D; concave lens
power - 0.25 D; convex lens
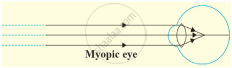
In Myopia the human eye _______.
cannot see nearby objects distinctly
cannot see distant objects clearly
cannot see nearby as well as distant objects clearly
can see nearby as well as distant objects clearly
Due to elongation of _______ and increase in curvature of the eye lens, a person cannot see distant objects clearly.
eyeball
pupil
eyelid
cornea
In hypermetropia human eye _______.
can see distant objects clearly
can see nearby objects distinctly
cannot see nearby as well as distant objects clearly
can see nearby as well as distant objects clearly
Bifocal lens is required to correct _______ defect.
myopia
hypermetropia
presbyopia
none of these
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
5
10
20
60
_______ is a combination of two convex lenses with small focal length.
simple microscope
compound microscope
telescope
none of these
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Find the correlation.
Find the correlation.
Convex lens : converging : : concave lens : _______
Nearsightedness: elongated eyeball : : farsightedness: _______
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : _______
Nearsightedness : concave lens : : farsightedness : _______
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : _______
Focal length : metre : : power of lens : _______
 : Concave lens : :
: Concave lens : : 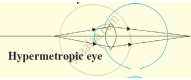 : ______
: ______
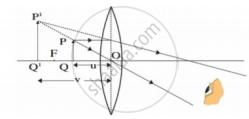 : Object near the lens : : ______ :
: Object near the lens : : ______ : 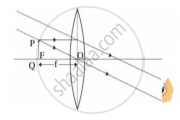
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Find odd one out.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Focal length
Radius of curvature
Image distance
Size of image
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Simple microscope
Compound microscope
Telescope
Prism
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Eye lens
Retina
Cerebellum
Cornea
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Object distance
Image distance
Focal length
Principal axis
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Eye piece
Magnifier
Kaleidoscope
Telescope
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Write the name
Write the name.
The distance between focus and optical centre.
Write the name.
The part of human eye that transmits electrical signals to the brain.
Write the name.
The lens used in simple microscope.
Name the capacity of the eye lens to change its focal length as per need.
Write the name.
The defect of eye occurring due to ageing
Write the name.
The fleshy screen behind cornea.
Write the name.
The screen with light sensitive cells in human eye.
Write the name.
The sensation on the retina persists for a while is
Write the name.
The persons which are unable to distinguish between different colours
Write the name.
The imaginary line passing through two optical centres of lens
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Right or Wrong sentence
Convex magnifying glass is called divergent magnifying glass and concave magnifying glass is called converging magnifying glass.
Right
Wrong
The image of the object in the human eye is formed on the cross screen.
Right
Wrong
Hypermetropia can be corrected using concave lens of proper focal length.
Right
Wrong
When the incident ray is parallel to the principal axis, the refracted ray passes through the principal focus.
Right
Wrong
The image of an object at an infinite distance is obtained in a real and erect form through a convex magnifying glass.
Right
Wrong
The power of the magnifying glass depends on the distance of the magnifying glass from object.
True
Wrong
The lens of the eye is flattened when looking at nearby objects.
Right
Wrong
For a healthy human eye, the distant point is infinite distance.
Right
Wrong
Vision defect that increases distance between the lens of the eye and retina of the eye is termed as myopia.
Right
Wrong
The virtual image of object seen by the eye depends on the angle subtended by the object with the eye.
Right
Wrong
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Write an Explanation
Write an Explanation.
Centre of curvature of the lens
Write an Explanation.
The optical centre of the lens
Write an Explanation.
Principal focus
Write an Explanation.
Focal length
Write an Explanation.
Principal axis
Write an Explanation.
Minimum distance of distinct vision
Write an Explanation.
Farthest distance of distinct vision
Write an Explanation.
Magnification
Write an Explanation.
Power of accommodation
Write an Explanation.
Persistence of vision
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Write scientific reasons
Write scientific reason.
A convex lens is called a converging lens.
Write scientific reason.
Nearsightedness, this defect can be corrected by using spectacles with concave lens.
Write scientific reason.
Farsightedness, this defect can be corrected by using convex lens.
Write scientific reason.
Adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
Write scientific reason.
Presbyopia effect is more common in people over 40 years of age.
Give scientific reason.
Simple microscope is used for watch repairs.
Give scientific reason:
One can sense colours only in bright light.
Write scientific reason.
The movie cannot be enjoyed if seat of a viewer is too close to the screen in the cinema.
Give scientific reason:
We cannot clearly see an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Distinguish between
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
Distinguish between:
Farsightedness and Nearsightedness.
Distinguish between:
Myopia - Presbyopia
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Answer the Following
Find the power of a convex lens of focal length of + 25 cm.
If focal length of a convex lens is 20 cm at what is the power of the lens?
If each two concave lenses of focal length 30 cm are kept in contact with each other what will be the power of combination?
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 12 cm, find out at what distance image will be formed from the lens and what is the nature of image.
5 cm high object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a converging lens of focal length of 20 cm. Determine the position, size and type of the image.
An object is placed vertically at a distance of 20 cm from a convex lens. If the height of the object is 5 cm and the focal length of the lens is 10 cm, what will be the position, size and nature of the image? How much bigger as compared to the object?
Two convex lenses of focal length 30 cm and 10 cm each are kept in contact with each other. Find the power of their combination.
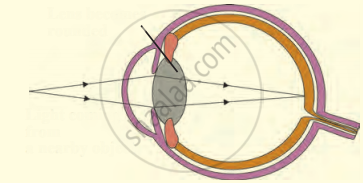
The following figure show the change in the shape of the lens while seeing distant and nearby objects. Complete the figures by correctly labelling the diagram.
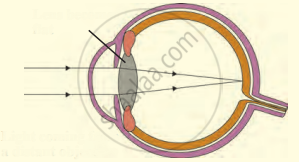
The following figure show the change in the shape of the lens while seeing distant and nearby objects. Complete the figures by correctly labelling the diagram.
Write the function of the human eye and label parts of the figure given below.

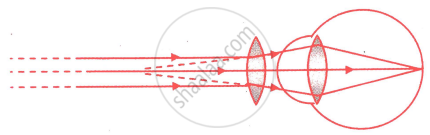
Observe the given below the figure, correct it and explain and write about the concept depicted in this figure.
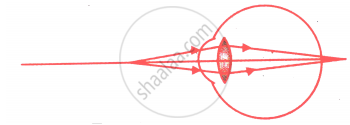
Given below is a diagram showing a defect of vision. Name the defect of vision and draw an accurately labelled diagram to correct this defect.
Write law in a given figure.

Write law in a given figure.
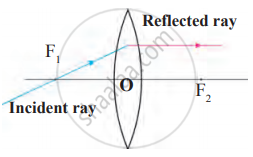
Write law in a given figure.
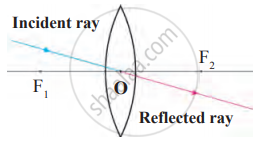
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.

- Where is the above type of lens construction used?
- What type of image is formed by an objective lens?
- What happens instead of placing at Fo if the object is placed in between O and Fo?
Identify and explain concepts given in this diagram.
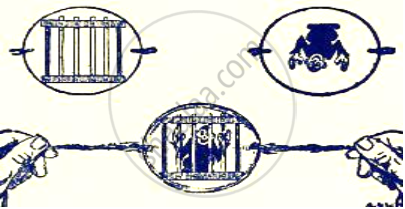
Complete the paragraph by choosing the right options given below.
(minimum, near point, 25 cm, farthest, farthest distance, far point)
The _______ distance of an object from a normal eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye, is called the minimum distance of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye, for a normal human eye, the near point is at _______. The _______ distance of an object from a human eye, at which it is clearly visible without stress on the eye is called _______ of distinct vision. The position of the object at this distance is called the _______ of the eye.
Choose the correct option from the bracket and complete the stanza.
(colour blind, actual, conical, light-sensitive, rodlike, colours)
The retina in our eyes is made up of many _______ cells. These cells are shaped like a rod and like a cone. The _______ cells respond to the intensity of light and give information about the brightness or dimness of the object to the brain. The _______ cells respond to the colour and give information about the colour of the object to the brain. Brain processes all the information received and we see the _______ image of the object. Rod like cells respond to the faint light also but ______ cells do not. Some people lack conical cells responding to certain colours. These persons cannot recognize those colours or cannot distinguish between different ______. These persons are said to be ______.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC 7 Lenses Answer the following questions
Explain with a ray diagram the position, size, and nature of the various image formed by convex lenses.
An object is at infinity.
Explain with a ray diagram the position, size, and nature of the various images formed by the convex lens.
An object beyond 2F1.
Explain with a ray diagram the position, size, and nature of the various images formed by a convex lens.
An object at 2F1.
Explain with a ray diagram the position, size, and nature of the various images formed by a convex lens.
An object is in between F1 and 2F1
Explain with a ray diagram the position, size, and nature of the various images formed by a convex lens.
Object at focus F1
Explain with a ray diagram the position, size, and nature of the various images formed by a convex lens.
Object between F1 and O
Solutions for 7: Lenses
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 7 - Lenses SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 7 - Lenses - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-and-technology-1-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 7 - Lenses
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 7 (Lenses) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. SCERT Maharashtra textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 7 Lenses are Power of a Lens, Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia, Convex Lens, Concave Lens, Spherical Lens, Images Formed by Convex Lenses, Combination of Lenses, Human Eye, Working of the Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness, Images Formed by Concave Lenses, Sign Convention, Lens Formula, Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses, Persistence of Vision, Concept of Lenses.
Using SCERT Maharashtra Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC solutions Lenses exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in SCERT Maharashtra Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC students prefer SCERT Maharashtra Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Lenses Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC additional questions for Mathematics Science and Technology 1 [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
