Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : _______
उत्तर
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : Number of convex lenses two
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student focuses the image of a well-illuminated distant object on a screen using a convex lens. After that, he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen by adjusting the lens.
(i) In which direction, towards the screen or away from the screen, does he move the lens?
(ii) What happens to the size of the image? Does it decrease or increase?
(iii) What happens to the image on the screen when he moves the object very close to the lens?
A student has obtained a magnified image of a flame on a screen using a convex lens. To draw the corresponding ray diagram to show the image formation, which of the following two rays whose paths after refraction are shown, should he select ?
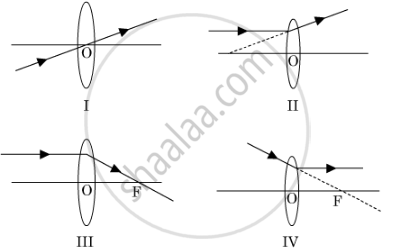
(A) I and II
(B) II and III
(C) III and IV
(D) I and III
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens?
An object AB is placed between O and F1 on the principal axis of a converging lens as shown in the diagram.
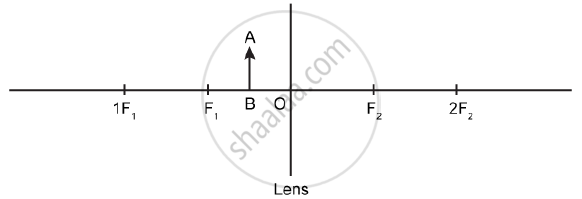
Copy the diagram and by using three standard rays starting from point A, obtain an image of the object AB.
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find :
1) the position of the image
2) nature of the image
A beam of light travelling in a rectangular glass slab emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
f the image formed by a convex lens is of the same size as that of the object, what is the position of the image with respect to the lens?
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f in front of a convex lens. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image. State two characteristics of the image formed.
A burning candle whose flame is 1.5 cm tall is placed at a certain distance in front of a convex lens. An image of candle flame is received on a white screen kept behind the lens. The image of flame also measures 1.5 cm. If f is the focal length of convex lens, the candle is placed:
(a) at f
(b) between f and 2f
(c) at 2f
(d) beyond 2f
What is the position of image when an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm?
Which of the above two cases illustrates the working of a magnifying glass?
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
Which causes more bending (or more refraction) of light rays passing through it : a convex lens of long focal length or a convex lens of short focal length?
The focal lengths of four convex lenses P, Q, R and S are 20 cm, 15 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm, respectively. The lens having greatest power is :
(a) P
(b) Q
(c) R
(d) S
A convex lens of focal length 10 cm is placed in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. The focal length of this combination of lenses will be:
(a) +10 cm
(b) +20 cm
(c) −10 cm
(d) −20 cm
What type of lens is used to correct
hypermetropia
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
A student places a 8.0 cm tall object perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. He obtains a sharp image of the object on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. What will be the nature (inverted, erect, magnified, diminished) of the image he obtains on a screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find: The position of image
If an object is placed in front of a convex lens beyond 2F1, then what will be the position, relative size, and nature of an image which is formed? Explain with a ray diagram.
What is the difference between a double convex and a bi-convex lens?
Draw a diagram to show the convergent action of a convex lens by treating it as a combination of glass block and two triangular glass prisms, with the aid of two parallel incident rays.
Can one bum a piece of paper in daylight by just using a convex lens instead of a match or any direct flame? Support your answer with the help of an appropriate ray diagram.
For a specific glass lens f = 0.5 m. This is the only information given to the student. Which type of lens is given to him and what is its power?
Object at 2F1 of a convex lens : Image at 2F2 : : Object at F1 : _______
Differentiate convex lens and concave lens.
Convex lens is also known as ______.
- In which type of microscope do you find the lens arrangement as shown in the following diagram?

- Write about the working and the use of this microscope.

The above image shows a thin lens with a focal length of 5m.
- What is the kind of lens shown in the above figure?
- If a real inverted image is to be formed by this lens at a distance of 7m from the optical centre, then show with calculation where should the object be placed.
- Draw a neatly labelled diagram of the image formation mentioned in (ii).
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex lens.
