Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : _______
Solution
Simple microscope : Number of convex lens one : : compound microscope : Number of convex lenses two
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A student places a candle flame at a distance of about 60 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm and focuses the image of the flame on a screen. After that he gradually moves the flame towards the lens and each time focuses the image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-toward or away from the lens, does he move the screen to focus the image?
(b) How does the size of the image change?
(c) How does the intensity of the image change as the flame moves towards the lens?
(d) Approximately for what distance between the flame and the lens, the image formed on the screen is inverted and of the same size?
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size as the object is obtained using a convex lens?
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from an optically denser medium into air.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a refracted ray of light.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its virtual, erect and magnified image?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are refracted by a convex lens to a point called the ........
Explain with the help of a diagram, why the convex lens is also called a converging lens.
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity (considerable distance) in front of a convex lens. State three characteristics of the image so formed.
Three convex lenses are available having focal lengths of 4 cm, 40 cm and 4 m respectively. Which one would you choose as a magnifying glass and why?
An object is placed f and 2f of a convex lens. Which of the following statements correctly describes its image?
(a) real, larger than the object
(b) erect, smaller than the object
(c) inverted, same size as object
(d) virtual, larger than the object
In order to obtain a real image twice the size of the object with a convex lens of focal length 15 cm, the object distance should be:
(a) more than 5 cm but less than 10 cm
(b) more than 10 cm but less than 15 cm
(c) more than 15 cm but less than 30 cm
(d) more than 30 cm but less than 60 cm
A convex lens of focal length 0.10 m is used to form a magnified image of an object of height 5 mm placed at a distance of 0.08 m from the lens. Calculate the position, nature and size of the image.
An object 3 cm high is placed 24 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find by calculations, the position, height and nature of the image.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.15 m
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Rewrite the image distances in the correct order.
Which type of lenses are:
thicker in the middle than at the edges?
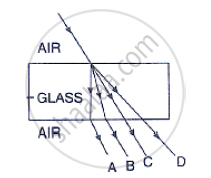
In figure , name the ray which represents the correct path of light while emerging out through
a glass block.
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a convex lens. Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through the lens.
The focal length of a thin convex lens is ______ than that of a thick convex lens.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object. Name the lens.
When you focus the image of a distant flag, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image as it appears on the screen is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
A teacher sets up the stand carrying a convex lens of focal length 15 cm at 42.7 cm mark on the optical bench. He asks four students A, B, C and D to suggest the position of screen on the optical bench so that a distinct image of a distant tree is obtained almost immediately on it. The positions suggested by the students were as
A. 12.7 cm
B. 29.7 cm
C. 57.7 cm
D. 72.7 cm
The correct position of the screen was suggested by
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
A student places a 8.0 cm tall object perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. He obtains a sharp image of the object on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. What will be the nature (inverted, erect, magnified, diminished) of the image he obtains on a screen? Draw ray diagram to justify your answer.
A student focussed the image of a distant object using a device ‘X’ on a white screen ‘S’ as shown in the figure. If the distance of the screen from the device is 40 cm, select the correct statement about the device.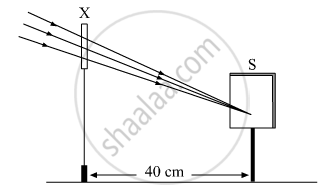
(A) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 20 cm.
(B) The device X is a concave mirror of focal length 40 cm.
(C) The device X is a convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm.
(D) The device X is a convex lens of focal length 40 cm.
List four properties of the image formed by a convex mirror.
For finding the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object, one should use as the object.
(1) a well lit distant tree
(2) window grill in the class room
(3) any distant tree
(4) a lighted candle kept at the other end of the table.
(a) What type of a lens can be used as a magnifying glass?
(b) Show by a ray diagram the formation of a real image by simple magnifying lens.
Point out the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of photographic camera.
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
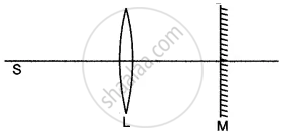
Define the principal focus of a convex lens.
_______ times larger images can be obtained by using a simple microscope.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
- In which type of microscope do you find the lens arrangement as shown in the following diagram?

- Write about the working and the use of this microscope.
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex lens.
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex Lens
Distinguish between:
Concave lens and Convex lens
