Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of photographic camera.
Solution
Object is in between infinity and 2F1. Image is formed between F2 and 2F1. Image is real; inverted and diminished.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A student is using a convex lens of focal length 18 cm to study the image formation by it for the various positions of the object. He observes that when he places the object at 27 cm, the location of the image is at 54 cm on the other side of the lens. Identify from the following diagram the three rays that are obeying the laws of refraction and may be used to draw the corresponding ray diagram.
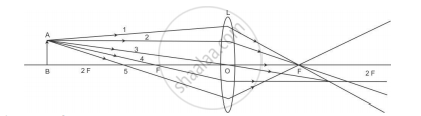
(A) 1, 2 and 4
(B) 1, 3 and 5
(C) 2, 4 and 5
(D) 2, 3 and 4
A convex lens of focal length 15 cm produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a) at a distance of 15 cm
(b) between 15 cm and 30 cm
(c) at less than 15 cm
(d) beyond 30 cm
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What is the focal length of this lens?
What would be the diameter of the image of the flower on the film?
The diagrams (a) and (b) in Figure below show the refraction of a monochromatic ray of light through a parallel sided glass block and a prism respectively. In each diagram, label the incident, refracted emergent rays and the angle of deviation.

Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image-distance (v) with object-distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow without doing any calculations:
| S. No. | Object-Distance u (cm) |
Image-Distance v (cm) |
| 1 | –60 | +12 |
| 2 | –30 | +15 |
| 3 | –20 | +20 |
| 4 | –15 | +30 |
| 5 | –12 | +60 |
| 6 | –9 | +90 |
(a) What is the focal length of the convex lens? State reason for your answer.
(b) For what object-distance (u) is the corresponding image-distance (v) not correct? How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(c) Choose an appropriate scale to draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
Write the three characteristics of the image formed by a convex lens of focal length 20 cm for the object at distance (i) 10 cm, (ii) 30 cm, (iii) 40 cm, (iv) 60 cm from the lens.
Which lens can produce a real and inverted image of an object?
A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the holes on the other face of the box as show in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
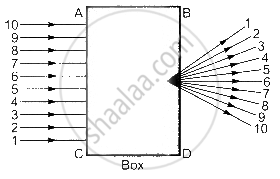
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
