Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain with the help of a diagram, why the convex lens is also called a converging lens.
Solution
A convex lense is outwardly curved and causes the light to pass through it and converge or concentrate to a point. Think of a magnifying glass that is used to burn something. The light that passes through it concentrates to a point, and this convergence is used to burn things. See the diagram given below.

RELATED QUESTIONS
An object 5 cm is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image.
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

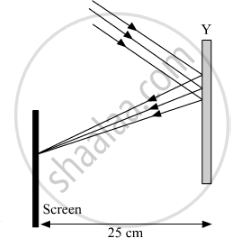
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
f the image formed by a convex lens is of the same size as that of the object, what is the position of the image with respect to the lens?
How could you find the focal length of a convex lens rapidly but approximately?
A convex lens of focal length 6 cm is held 4 cm from a newspaper which has print 0.5 cm high. By calculation, determine the size and nature of the image produced.
If the object is moved to a point only 3 cm away from the lens, what is the new position, height and nature of the image?
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
Which of the object distances gives the biggest image?
A light ray does not bend at the boundary in passing from one medium to the other medium if the angle of incident is:
A concave mirror and convex lens are held in water. What changes, if any, do you expect in their focal length?
Define the principal focus of a convex lens.
