Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a convex lens. Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through the lens.
Solution
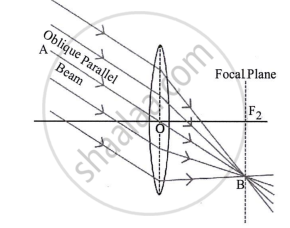
A convex lens causes a parallel oblique beam of light to be refracted, as shown in the above diagram.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Study the given ray diagrams and select the correct statement from the following:

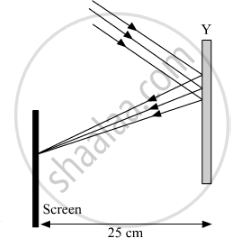
(A) Device X is a concave mirror and device Y is a convex lens, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(B) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 10 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(C) Device X is a concave lens and device Y is a convex mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
(D) Device X is a convex lens and device Y is a concave mirror, whose focal lengths are 20 cm and 25 cm respectively.
An object AB is placed between O and F1 on the principal axis of a converging lens as shown in the diagram.
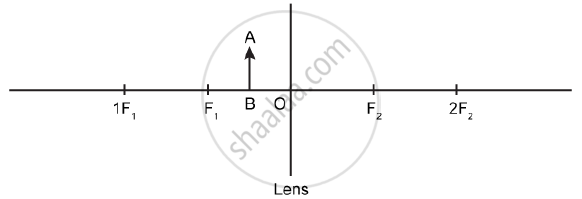
Copy the diagram and by using three standard rays starting from point A, obtain an image of the object AB.
A beam of light travelling in a rectangular glass slab emerges into air. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path.
What type of lens would you use as a magnifying glass? How close must the object be to the lens?
You eye contains a convex lens. Why is it unwise to look at the sun?
What type of images can a convex lens make?
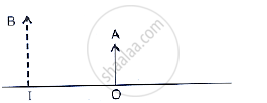
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens.
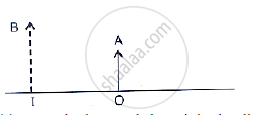
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens. State three characteristics of the image.
Why do we say that the ‘2F’ and ‘F’ points of a convex lens can be regarded as a sort of ‘turning points’ as far as the nature of the image formed by it is concerned?
Define the principal focus of a convex lens.
