Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Force
2: Work, Energy and Power
3: Machines
LIGHT
4: Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
▶ 5: Refraction through a Lens
6: Spectrum
SOUND
7: Sound
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
8: Current Electricity
9: Household Circuits
10: Electro-Magnetism
HEAT
11: Calorimetry
MODERN PHYSICS
12: Radioactivity
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Refraction through a Lens Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Refraction through a Lens - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Refraction through a Lens
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of CISCE Selina for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 5 Refraction through a Lens EXERCISE - 5 (A) [Pages 109 - 110]
What is lens?
Name the different kinds of lenses.
Draw diagrams to illustrate two kinds of lens.
State differences between a convex and a concave lens in their
- Appearance, and
- action on the incident light.
Which lens is converging:
An equiconcave lens
An equiconvex lens
Which lens is converging:
A concavo-convex lens
A convexo-concave lens
Out of the two lenses, one concave and the other convex, state which one will show the divergent action on a light beam. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
Show by a diagram the refraction of two light rays incident parallel to the principal axis on a convex lens by treating it as a combination of a glass slab and two triangular glass prisms.
Show by a diagram, the refraction of two light rays incident parallel to the principal axis on a concave lens by treating it as a combination of a glass block and two triangular glass prisms.
How does the action of a convex lens differ from that of a concave lens on a parallel beam of light incident on them? Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
Explain optical centre of a lens with the help of proper diagram(s).
A ray of light incident at a point on the principal axis of a convex lens passes undeviated through the lens.
- What special name is given to this point on the principal axis?
- Draw a labelled diagram to support your answer in part (a).
State the condition when a lens is called an equi-convex or equi-concave.
Define the term principal foci of a convex lens and illustrate your answer with the aid of proper diagrams.
Define the term principal foci of a concave lens and show them with the help of proper diagrams.
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a concave lens.
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
A ray of light, after refraction through a concave lens emerges parallel to the principal axis.
- Draw a ray diagram to show the incident ray and its corresponding emergent ray.
- The incident ray when produces meets the principal axis at a point F. Name the point F.
A ray of light after refraction through a convex lens emerges parallel to principal axis.
- Draw a ray diagram to show it.
- The incident ray passes through a point F on the principal axis. Name the point F.
A beam of light incident on a convex lens parallel to its principal axis converges at a point F on the principal axis. Name the point F. Draw a ray diagram to show it.
A beam of light incident on a thin concave lens parallel to its principal axis diverges and appears to come from a point F on the principal axis. Name the point F. Draw a ray diagram to show it.
What do you mean by focal plane of a lens?
State the condition of the following:
A lens has both its focal lengths equal.
State the condition of the following:
A ray passes undeviated through the lens.
A parallel oblique beam of light falls on a convex lens. Draw a diagram to show the refraction of light through the lens.
A parallel, oblique beam of light falls on a concave lens. Draw a diagram to show refraction of light through the lens.
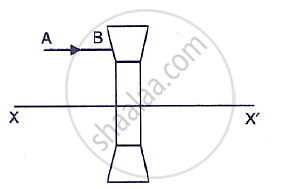
The diagram below shows a lens as a combination of a glass slab and two prisms.

- Name the lens formed by the combination.
- What is the rays the line XX’ called?
- Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray AB after passing through the lens.
- The final emergent ray will either meet XX’ at a point or appear to come from a point on XX’. Label the point as F. What is this point called?
The diagram below shows a lens as a combination of a glass slab and two prisms.
- Name the lens formed by the combination.
- What is the line XX’ called?
- Complete the path of the incident ray AB after passing through the lens.
- The final emergent ray either meets XX’ at a point or appears to come from a point on XX’. Label it as F. What is this point called?
In the following figure (a) and (b), F1 and F2 are positions of the two foci of thin lenses. Draw the path taken by the light ray AB after it emerges from each lens.
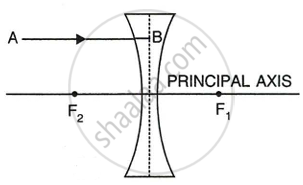 |
| (a) |
 |
| (b) |
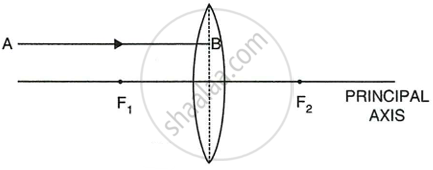
In figure, (a) and (b), F1 and F2 are the two foci of thin lenses and AB is the incident ray. Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray AB after refraction through each lens.
 |
| (a) |
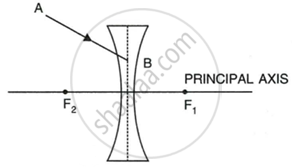 |
| (b) |
If half part of a convex lens is covered, the focal length ______ change, but the intensity of image ______.
A convex lens is placed in water. Its focal length will ______.
The focal length of a thin convex lens is ______ than that of a thick convex lens.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
A ray of light after refraction through a lens emerges parallel to the principal axis of the lens. The incident ray either passes through ______.
its optical centre
its first focus
its second focus
its centre of curvature of the first surface
A ray of light incident on a lens parallel to its principal axis, after refraction passes through or appears to come from ______.
Its first focus
Its optical entre
Its second focus
The centre of curvature of its second surface
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 5 Refraction through a Lens EXERCISE - 5 (B) [Pages 119 - 121]
What are the three principal rays that are drawn to construct the ray diagram for the image formed by a lens? Draw diagrams to support your answer.
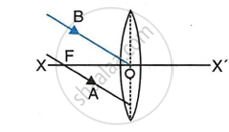
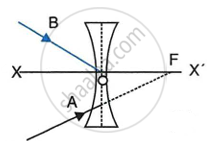
In the diagram below, XX’ represents the principal axis, O the optical centre and F the focus of the lens. Complete the path of rays A and B as they emerge out of the lens.
 |
 |
| (a) | (b) |
Where must a point source of light be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain a parallel beam of light?
Study the diagram given below.
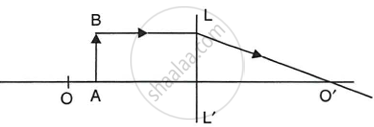
- Name the lens LL’.
- What are the points O and O’ called?
- Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
- State the three characteristics of the image.
- Name a device in which this action of lens is used.
Study the diagram below.
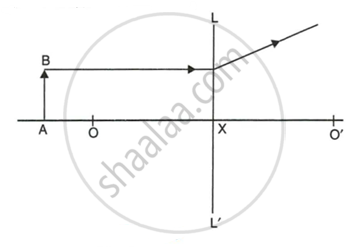
- Name the lens LL’.
- What are the points O and O' called ?
- Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
- State three characteristics of the image.
The following diagram shows an object AB and a converging lens L with foci F1 and F2. Draw two rays from the object AB and complete the diagram to locate the position of the image CD. Also mark on the diagram the position of eye from where the image can be viewed.
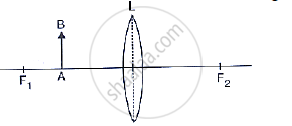
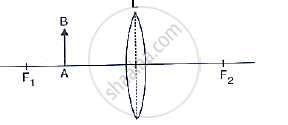
The following diagram shows an object AB and a converging lens L with foci F1 and F2 State three characteristics of the image in relation to the object.
The diagram given below shows the position of an object OA in relation to a converging lens L whose foci are at F1 and F2.
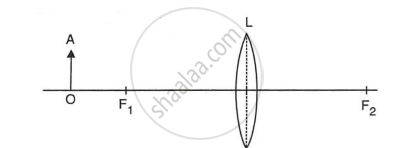
- Draw two rays to locate the position of the image.
- State the position of the image with reference to the lens.
- Describe three characteristics of the image.
- Describe how the distance of the image from the lens and its size change as the object is moved towards F1.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it beyond 2F2 of the lens. Where is the object placed?
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. State three characteristics of the image.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. Where is the object placed in front of the lens?
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. Draw a diagram to illustrate it.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. State two more characteristics of the image.
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Name the type of lens.
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Where is the object placed in relation to the lens?
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation.
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Name the device which uses this principle.
A lens forms an image between the object and the lens. Name the lens.
A lens forms an image between the object and the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of such an image.
A lens always forms an image between the object and the lens. State three characteristics of the image.
Classify as real or virtual, the image of a candle flame formed on a screen by a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate how the image is formed.
Show by a ray diagram that a diverging lens cannot form a real image of an object placed anywhere on its principal axis.
Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens can form a real and enlarged image of an object.
A lens forms an upright and diminished image of an object when the object is placed at its focal point. Name the lens and draw a ray diagram to show the image formation.
Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens is used as a magnifying glass to observe a small object. Mark on your diagram the foci of the lens and the position of the eye.
Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens can form an image of the sun. Hence give a reason for the term ‘burning glass’ for a converging lens used in this manner.
A lens forms an inverted image of an object. Name the kind of lens.
A lens forms an inverted image of an object. What is the nature of the image real or virtual?
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object. Name the lens.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation.
- Name the lens which always forms an erect and virtual image.
- State whether the image in part (a) is magnified or diminished.
Can a concave lens form an image of size two times that of the object? Give reason.
Give two characteristics of the image formed by a concave lens.
Give two characteristics of the virtual image formed by a convex lens.
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is at infinity?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is of the same size as the object?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is upright and enlarged?
Complete the following table:
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| Convex | Between optical centre and focus | ||
| Convex | At focus | ||
| Concave | At infinity | ||
| Concave | At any distance |
State the changes in the position, size and nature of the image when the object is brought from infinity up to the convex lens. Illustrate your answer by drawing ray diagrams.
State the changes in the position, size and nature of the image when the object is brought from infinity up to a concave lens. Illustrate your answer by drawing ray diagrams.
An object is placed at a distance of more than 40 cm from a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The image formed is real, inverted and ______.
An object is placed at a distance 2f from a convex lens of focal length f. The size of the image formed is ______ that of the object.
An object is placed at a distance 5 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. The image formed is virtual, upright and _____.
State whether the following statements are 'true' or 'false':
A convex lens has a divergent action and a concave lens has a convergent action.
True
False
A concave lens, if kept at a proper distance from an object, can form its real image.
True
False
A ray of light incident parallel to the principal axis of a lens, passes undeviated after refraction.
True
False
A ray of light incident at the optical centre of lens, passes undeviated after refraction.
True
False
A concave lens forms a magnified or diminished image depending on the distance of an object from it.
True
False
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
For an object placed at a distance 20 cm in front of a convex lens, the image is at a distance 20 cm behind the lens. The focal length of the convex lens is ______.
20 cm
10 cm
15 cm
40 cm
For the object placed between the optical centre and focus of a convex lens, the image is ______.
real and enlarged
real and diminished
virtual and enlarged
virtual and diminished
A concave lens forms the image of an object which is ______.
virtual, inverted and diminished
virtual, upright and diminished
virtual, inverted and enlarged
virtual, upright and enlarged
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 5 Refraction through a Lens EXERCISE - 5 (C) [Pages 126 - 127]
State the sign convention to measure the distances for a lens.
The focal length of a lens is positive. In this case, state the kind of lens.
The focal length of a lens is negative. In this case, state the kind of lens.
Write the lens formula explaining the meaning of the symbols used.
What do you understand by the term magnification?
Write an expression for magnification for a lens, explaining the meaning of the symbols used.
What information about the nature of image is real or virtual, do you get from the sign of magnification + or -?
What information about the nature of image is erect or inverted, do you get from the sign of magnification + or -?
Define the term power of a lens.
In what unit is the power of a lens expressed?
How is the power of a lens related to its focal length?
How does the power of a lens change if its focal length is doubled?
How is the sign (+ or -) of power of a lens related to its divergent or convergent action?
The power of a lens is negative. State whether it is convex or concave.
Which lens has more power a thick lens or a thin lens?
A lens of power +2·5D is kept in contact with another lens of power -2·5D. Draw the path of a ray passing through the lens combination.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
If the magnification produced by a lens is - 0.5, the correct statement is ______.
The lens is concave
The image is virtual
The image is magnified
The images is real and diminished formed by a convex
The correct lens formula is ______.
`1/"u" + 1/"v" = 1/"f"`
`1/"u" - 1/"v" = 1/"f"`
`"f" = "uv"/"u - v"`
f = `("u + v")/"uv"`
On reducing the focal length of a lens, its power ______.
Decreases
Increases
Does not change
First increases then decreases.
The lens of power + 1·0 D is ______.
Convex of focal length 1·0 cm
Convex of focal length 1·0 m
Concave of focal length 1·0 cm
Concave of focal length 1·0 m.
NUMERICALS
- At what position a candle of length 3 cm be placed in front of a convex lens so that its image of length 6 cm be obtained on a screen placed at distance 30 cm behind the lens?
- What is the focal length of lens in part (a)?
A concave lens forms the image of an object kept at a distance 20 cm in front of it, at a distance 10 cm on the side of the object.
- What is the nature of the image?
- Find the focal length of the lens.
The focal length of a convex lens is 25 cm. At what distance from the optical centre of the lens an object be placed to obtain a virtual image of twice the size?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens of focal length 0.12 m to obtain a real image of size three times the size of the object, on the screen?
An illuminated object lies at a distance 1.0 m from a screen. A convex lens is used to form the image of the object on a screen placed at a distance of 75 cm from the lens. Find:
- the focal length of the lens, and
- the magnification.
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance 15 cm from it, at a distance 60 cm in front of it. Find the focal length.
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance 15 cm from it, at a distance 60 cm in front of it. Find the magnification.
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance 15 cm from it, at a distance 60 cm in front of it. Find the nature of image.
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance of 45 cm from it on a screen placed at a distance 90 cm on the other side of it. Name the kind of lens.
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance of 45 cm from it on a screen placed at a distance 90 cm on the other side of it. Find:
- the focal length of lens,
- the magnification of the image.
An object is placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 20 cm.
- Find the position of the image, and
- the magnification of the image.
A convex lens forms an inverted image of size same as that of the object which is placed at a distance 60 cm in front of the lens. Find:
- The position of the image, and
- The focal length of the lens.
A concave lens forms an erect image of `1/3`rd the size of the object which is placed at a distance 30 cm in front of the lens. Find:
- the position of image, and
- the focal length of the lens.
The power of a lens is +2.0 D. Find its focal length and state the kind of lens.
Express the power (with sign) of a concave lens of focal length 20 cm.
The focal length of a convex lens is 25 cm. Express its power with sign.
The power of a lens is -2.0 D. Find its focal length and its kind.
The magnification by a lens is -3. Name the lens and state how are u and v related?
The magnification by a lens is +0.5. Name the lens and state how are u and v related?
A concave lens has a focal length 30 cm. Find the position and magnification (m) of the image for an object placed in front of it at distance 30 cm. State whether the image is real or virtual?
Find the position and magnification of the image of an object placed at distance of 8.0 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 10.0 cm. Is the image erect or inverted?
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 5 Refraction through a Lens EXERCISE- 5 (D) [Pages 131 - 132]
What is a magnifying glass?
State two uses of magnifying glass.
Draw a neat labelled ray diagram to show the formation of an image by a magnifying glass. State three characteristics of the image.
Where is the object placed with respect to the principal focus of a magnifying glass, so as to see its enlarged image? Where is the image obtained?
Write an expression for the magnifying power of a simple microscope. How can it be increased?
State two applications of a convex lens.
State two applications of a concave lens.
Describe in brief how would you determine the approximate focal length of a convex lens.
The following diagram shows the experimental set up for the determination of focal length of a lens using a plane mirror.
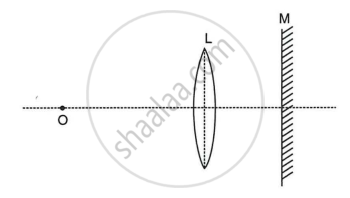
- Draw two rays from the point O of the object to show the formation of image I at O itself.
- What is the size of the image I?
- State two more characteristics of the image I.
- Name the distance of the objects O from the optical centre of the lens.
- To what point will the rays return if the mirror is moved away from the lens by a distance equal to the focal length of the lens?
Describe how you would determine the focal length of a converging lens, using a plane mirror and one pin. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.
How will you differentiate between a convex and a concave lens by looking at
- a distant object,
- a printed page?
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
A magnifying glass forms ______.
A real and diminished image
A real and magnified image
A virtual and magnified image
A virtual and diminished image
The maximum magnifying power of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm can be ______.
25
10
1
6
Solutions for 5: Refraction through a Lens
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Refraction through a Lens Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Refraction through a Lens - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Refraction through a Lens
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 5 (Refraction through a Lens) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 Refraction through a Lens are Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses, Concept of Lenses, Action of a Lens as a Set of Prisms, Spherical Lens, Refraction of Light Through the Equiconvex Lens and Equiconcave Lens, Guideline for Image Formation Due to Refraction Through a Convex and Concave Lens, Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image, Images Formed by Sperical Lenses, Concave Lens, Images Formed by Concave Lenses, Convex Lens, Images Formed by Convex Lenses, Differentiation Between Concave and Convex Lens, Sign Convention, Lens Formula, Power of a Lens, Magnifying Glass Or Simple Microscope, Experimental Determination of Focal Length of Convex Lens, Magnification Due to Spherical Lenses, Concept of Lenses, Action of a Lens as a Set of Prisms, Spherical Lens, Refraction of Light Through the Equiconvex Lens and Equiconcave Lens, Guideline for Image Formation Due to Refraction Through a Convex and Concave Lens, Formation of Image by Reflection: Real and Virtual Image, Images Formed by Sperical Lenses, Concave Lens, Images Formed by Concave Lenses, Convex Lens, Images Formed by Convex Lenses, Differentiation Between Concave and Convex Lens, Sign Convention, Lens Formula, Power of a Lens, Magnifying Glass Or Simple Microscope, Experimental Determination of Focal Length of Convex Lens.
Using Selina Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Refraction through a Lens exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Refraction through a Lens Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
