Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Force
2: Work, Energy and Power
3: Machines
LIGHT
4: Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
5: Refraction through a Lens
▶ 6: Spectrum
SOUND
7: Sound
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
8: Current Electricity
9: Household Circuits
10: Electro-Magnetism
HEAT
11: Calorimetry
MODERN PHYSICS
12: Radioactivity
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Spectrum Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Spectrum - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Spectrum
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CISCE Selina for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Spectrum EXERCISE - 6 (A) [Pages 137 - 138]
Name three factors on which the deviation produced by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you.
How does the speed of light in glass change on increasing the wavelength of light?
Which colour of white light travels fastest in glass?
Which colour of white light travels slowest, in glass?
Name the subjective property of light related to its wavelength.
What is the range of wavelength of the spectrum of white light in Å?
What is the range of wavelength of the spectrum of white light nm?
Write the approximate wavelengths for blue.
Write the approximate wavelength for red light.
The wavelengths of violet and red light are 4000 Å and 8000 Å respectively. Which of the two has the higher frequency?
Write the seven prominent colours present in white light spectrum in order of their increasing wavelength.
Name the seven prominent colours of the white light spectrum in order of their increasing frequencies.
Name four colours of the spectrum of white light which have wavelength longer than blue light.
Which colour of white light is deviated by a glass prism
- the most and
- the least?
The wavelengths for the light of red and blue colours are nearly 7·8 × 10-7 m and 4·8 × 10-7 m respectively.
Which colour has greater speed in glass?
Define the term dispersion of light.
Explain the cause of dispersion of white light through a prism.
Explain briefly, with the help of a neat labelled diagram, how white light gets dispersed by a prism. On which surface of a prism, there is both dispersion and deviation of light, and on which surface of the prism, there is only deviation of light ?
A ray of white light is passed through a glass prism and a spectrum is obtained on a screen.
- Name the seven colours of the spectrum in order.
- Do the colours have the same width in the spectrum?
- Which of the colour of the spectrum of white light deviates (i) the most, (ii) the least?
The diagram below shows the path taken by a narrow beam of yellow monochromatic light passing through an equiangular glass prism. If the yellow light is replaced by a narrow beam of white light incident at the same angle, draw another diagram to show the passage of white light through the prism and label it to show the effect of prism on the white light.
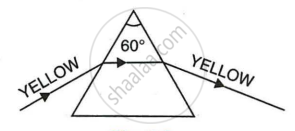
Fig shows a thin beam of white light from a source S striking on one face of a prism.
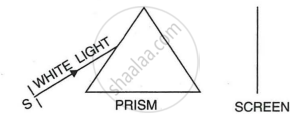
- Complete the diagram to show the effect of the prism on the beam and to show what is seen on the screen.
- If a slit is placed in between the prism and the screen to pass only the light of green colour, what will you then observe on the screen?
- What conclusion do you draw from the observation in part (b) above?
- A beam of monochromatic light undergoes minimum deviation through an equiangular prism, how does the beam pass through the prism, with respect to its base?
- If white light is used in the same way as in part (a) above, what change do you expect in the emergent beam?
- What conclusion do you draw about the nature of white light in part (b)?
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
When a white light ray falls on a prism, the ray at its first surface suffers ______.
No refraction
Only dispersion
Only deviation
Both deviation and dispersion
In the spectrum of white light by a prism, the colour at the extreme end opposite to the base of prism is ______.
Violet
Yellow
Red
Blue
The wavelength range of white light is ______.
4000 nm to 8000 nm
40 nm to 80 nm
400 nm to 800 nm
4 nm to 8 nm
NUMERICALS
Calculate the frequency of yellow light of wavelength 550 nm. The speed of light is 3 × 108 m/s-1.
The frequency range of visible light is from 3.75 × 1014 Hz to 7.5 × 1014 Hz. Calculate its wavelength range. Take speed of light = 3 × 108 m/s.
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Spectrum EXERCISE - 6 (B) [Pages 144 - 145]
- Give a list of at least five radiations, in the order of their increasing wavelength, which make up the complete electromagnetic spectrum.
- Name the radiation mentioned by you in part (a) which has the highest penetrating power.
Arrange the following radiations in the order of their increasing wavelength:
X-rays, infrared rays, ratio waves, gamma ray and microwaves.
Name the radiation which is used for satellite communication.
A wave has a wavelength of 10-3 nm. Name the wave.
A wave has a wavelength of 10-3 nm. State its one property different from light.
A wave has wavelength 50 Å.
- Name the wave.
- State its speed in vacuum.
- State its one use.
- Name the high energetic invisible electro-magnetic wave which helps in the study of structure of crystals.
- State one more use of the wave named in part (a).
State the name and the range of wavelength of the invisible electromagnetic waves beyond the red end of the visible spectrum.
Name three radiations and their wavelength range which are invisible and beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum.
Give the range of wavelength of the electromagnetic waves visible to us.
Name the region just beyond the red end.
Name the region just beyond the violet end, of the spectrum.
What do you understand by the invisible spectrum?
Name the radiation which can be detected by thermopile.
Name the radiation which can be detected by a solution of silver chloride.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with the ultraviolet rays.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with visible light.
State the approximate range of wavelength associated with infrared rays.
Name the radiations of wavelength just longer than 8 × 10-7m.
Name the radiations of wavelength just shorter than 4 × 10-7 m.
Name two electromagnetic waves of wavelength smaller than that of violet light.
State one use of gamma rays.
State one use of X-rays.
Give one use of microwaves.
Give one use of ultraviolet radiation.
Give one use of infrared radiations.
Give one use of gamma rays.
Name the waves of lowest wavelength.
Name the waves used for taking photographs in dark.
Name the waves produced by the changes in the nucleus of an atom.
Name the waves of wavelength nearly 0.1 nm.
Two waves A and B have wavelength 0.01 Å and 9000 Å respectively.
- Name the two waves.
- Compare the speeds of these waves when they travel in vacuum.
Name two sources, each of infrared radiations and ultraviolet radiations.
What are infrared radiations?
How can the presence of infrared Radiations be detected?
Give one use of infrared radiations.
What are ultraviolet radiations?
How are ultraviolet radiations detected?
State one use of ultraviolet radiations.
Give two properties of ultraviolet radiations which differ from the visible light.
Mention three properties of infrared radiations similar to the visible light.
Give two such properties of infrared radiations which are not true for visible light.
Name the material prism required for obtaining the spectrum of ultraviolet light.
Name the material prism required for obtaining the spectrum of infrared radiation.
Name the radiations which are absorbed by the green house gases in the earth's atmosphere.
State one harmful effect of the ultraviolet radiation.
State one harmful effect of the infrared radiation.
Give reason for the following:
Infrared radiations are used for photography in fog.
Give reason for the following:
Infrared radiations are used as signals during war.
Give reason for the following:
The photographic darkrooms are provided with infrared lamps.
Give reason for the following:
A rock salt prism is used instead of a glass prism to obtain the infrared spectrum.
Give reason for the following:
A quartz prism is required for obtaining the spectrum of ultraviolet light.
Give reason for the following:
Ultraviolet bulbs have a quartz envelope instead of glass.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The most energetic electromagnetic radiations are ______.
Microwaves
Ultraviolet waves
X-rays
Gamma rays
The source of ultraviolet light is ______.
Electric bulb
Red hot iron ball
Sodium vapour lamp
Carbon arc-lamp
A radiation P is focused by a proper device on the bulb of a thermometer. Mercury in the thermometer shows a rapid increase. The radiation P is ______.
Infrared radiation
Visible light
Ultra-violet radiation
X-rays
NUMERICALS
-
- Calculate the speed of the wave.
- Name the medium through which it is traveling.
The wavelength of X-rays is 0.01 Å. Calculate its frequency. State the assumption made, if any.
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 6 Spectrum EXERCISE - 6 (C) [Page 147]
Answer the following questions in your own words.
What is meant by scattering of light?
How does the intensity of scattered light depend on the wavelength of incident light? State conditions when this dependence holds.
When sunlight enters the earth’s atmosphere, state which colour of light is scattered
- the most and
- which the least.
A beam of blue, green, and yellow light passes through the earth's atmosphere. Name the colour which is scattered the least.
A beam of blue, green and yellow light passes through the earth's atmosphere. Name the colour which is scattered the most.
Which colour of white light is scattered the least? Give reason.
The danger signal is red. Why?
How would the sky appear when seen from the space (or moon)? Give reason for your answer.
What characteristic property of light is responsible for the blue colour of the sky?
The colour of sky, in direction other than of the sun, is blue. Explain.
Why does sun appear red at sunrise and sunset?
The sky at noon appears white. Give reason.
The clouds are seen white. Explain
Give reason why the smoke from fire looks white.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
In white light of sun, maximum scattering by the air molecular present in the earth’s atmosphere is for ______.
Red colour
Yellow colour
Green colour
Blue colour
To an astronaut in a space-ship, the earth appears ______.
White
Red
Blue
black
Solutions for 6: Spectrum
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Spectrum Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Spectrum - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 - Spectrum
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 6 (Spectrum) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 6 Spectrum are Deviation Produced by a Triangular Prism, Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum, Electromagnetic Spectrum, Colour in White Light with Their Wavelength and Frequency Range, Different Radiation of Electromagnetic Spectrum, Gamma Rays, X rays, Visible Light, Micro Waves, Radio Waves, Scattering of Light and Its Types, Applications of Scattering of Light, Ultraviolet Radiations, Infrared Radiations, Deviation Produced by a Triangular Prism, Dispersion of Light Through Prism and Formation of Spectrum, Electromagnetic Spectrum, Colour in White Light with Their Wavelength and Frequency Range, Different Radiation of Electromagnetic Spectrum, Gamma Rays, X rays, Visible Light, Micro Waves, Radio Waves, Scattering of Light and Its Types, Applications of Scattering of Light, Ultraviolet Radiations, Infrared Radiations.
Using Selina Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Spectrum exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Spectrum Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
