Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Force
2: Work, Energy and Power
3: Machines
LIGHT
4: Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
5: Refraction through a Lens
6: Spectrum
SOUND
▶ 7: Sound
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
8: Current Electricity
9: Household Circuits
10: Electro-Magnetism
HEAT
11: Calorimetry
MODERN PHYSICS
12: Radioactivity
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Sound Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Sound - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Sound
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of CISCE Selina for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Sound EXERCISE - 7 (A) [Pages 154 - 155]
What are mechanical waves?
Define amplitude term in relation to a wave.
Define frequency term in relation to a wave.
Define wavelength term in relation to a wave.
Define wave velocity term in relation to a wave.
A wave passes from one medium to another medium. Mention one property of the wave out of speed, frequency or wavelength which changes.
A wave passes from one medium to another medium. Mention one property of the wave out of speed, frequency or wavelength which does not change.
State two factors on which the speed of a wave travelling in a medium depends.
State two differences between light and sound waves.
What do you mean by reflection of sound? State one condition for the reflection of a sound wave. Name a device in which reflection of sound wave is used.
What is meant by an echo?
State two conditions necessary for hearing an echo.
A man is standing at a distance of 12 m from a cliff. Will he be able to hear a clear echo of his sound? Give a reason for your answer.
State two applications of echo.
Explain how the speed of sound can be determined by the method of echo.
What is meant by sound ranging?
Give one use of sound ranging.
Name the waves used for sound ranging. State one reason for their use.
Why are the waves mentioned by you not audible to us?
What is 'SONAR'?
State the principle on which SONAR is based.
State the use of echo in medical science/field.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The minimum distance between the source and the reflector in air. So that an echo is heard is approximately equal to ______.
10 m
17 m
34 m
50 m
To detect the obstacles in their path, bats produce ______.
Infrasonic waves
Ultrasonic waves
Electromagnetic waves
Radio waves
NUMERICALS
The wavelength of waves produces on the surface of water is 20 cm. If the wave velocity is 24 m s-1, calculate:
- the number of waves produced in one second, and
- the time in which one wave is produced.
Calculate the minimum distance in air required between the source of sound and the obstacle to hear an echo. Take speed of sound in air = 350 m s-1
What should be the minimum distance between source and reflector in water so that echo is heard distinctly?
(The speed of sound in water = 1400 m s-1)
A man standing 25 m away from a wall produces a sound and receives the reflected sound.
- Calculate the time after which he receives the reflected sound if the speed of the sound in air is 350 m/s-1.
- Will the man be able to hear a distinct echo? Explain the answer.
A RADAR sends a signal with a speed of 3 x 108 m s-1 to an aeroplane at a distance of 300 km from it. After how much time is the signal received back after reflection from the aeroplane?
A man standing 48 m away from a wall fires a gun. Calculate the time after which an echo is heard. (The speed of sound in air is 320 ms-1).
A ship on the surface of water sends a signal and receives it back from a submarine inside water after 4 s. Calculate the distance of the submarine from the ship. (The speed of sound in water is 1450 ms-1)
A pendulum has a frequency of 5 vibrations per second. An observer starts the pendulum and fires a gun simultaneously. He hears echo from the cliff after 8 vibrations of the pendulum. If the velocity of sound in air is 340 ms-1, find the distance between the cliff and the observer.
A person standing between the two vertical cliffs produces a sound. Two successive echoes are heard at 4 s and 6 s. Calculate the distance between the cliffs.
(Speed of sound in air = 320 ms-1)
A person standing at a distance x in front of a cliff fires a gun. Another person B standing behind the person A at a distance y from the cliff hears two sounds of the fired shots after 2s and 3s respectively. Calculate x and y (take speed of sound 320 m/s-1).
On sending an ultrasonic wave from a ship towards the bottom of a sea, the time interval between sending the wave and receiving it back is found to be 1.5 s. If the velocity of wave in sea water is 1400 m s-1, find the depth of the sea.
Figure below shows the distance-displacement graph of two waves A and B. Compare
- the amplitude,
- the wavelength of the two waves.

Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Sound EXERCISE-7 (B) [Pages 163 - 165]
What do you understand by free vibrations of a body?
Draw a graph between displacement and the time for a body executing free/natural vibrations.
Where can a body execute natural vibrations?
State one condition for a body to execute free/natural vibrations.
- Name one factor on which the frequency of sound emitted due to vibrations in an air column depends.
- How does the frequency depend on the factor stated in part (a).
State one way of increasing the frequency of a note produced by an air column.
State two ways of increasing the frequency of vibrations of a stretched string.
How does the frequency of sound given by a stretched string depend on its
- length,
- tension?
What adjustments would you make for tuning a stringed instrument for it to emit a note of a desired frequency?
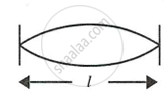
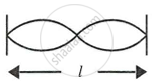
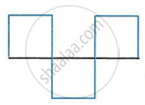
Fig. shows three ways in which a string of length l in an instrument can vibrate.
 |
 |
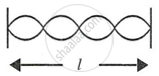 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) |
- Which of the diagram shows the principle note?
- Which vibration has the frequency four times that of the first?
- Which vibration is of the longest wavelength?
- What is the ratio of the frequency of the vibration in (i) and (ii)?
Explain why strings of different thicknesses are provided on a stringed instrument.
[Hint: Natural frequency of vibration of a stretched string is inversely proportional to the radius (or thickness) of string so notes of different frequencies can be produces by vibrating different strings.]
A blade, fixed at one end, is made to vibrate by pressing its other end and then releasing it. State one way in which the frequency of vibrations of the blade can be lowered.
How does the medium affect the amplitude of free/natural vibrations of a body?
What are damped vibrations? How do they differ from free vibrations? Give one example of each.
The following diagram shows the displacement – time graph of the vibrating body.

- Name the kind of vibrations
- Give one example of such vibrations.
- Why is the amplitude of vibrations gradually decreasing?
- What happens to the vibrations of the body after some time?
A tuning fork is vibrating in air. State whether the vibrations are natural or damped?
Draw a sketch showing the displacement of a body executing damped vibrations against time.
What are forced vibrations?
Give one example to illustrate forced vibrations.
On keeping the stem of a vibrating tuning fork on the surface of a table, a loud sound is heard. Give reason.
Distinguish between the free (or natural) and forced vibrations.
What is meant by resonance?
Describe a simple experiment to illustrate the phenomenon of resonance and explain it.
State the condition for the occurrence of resonance.
Resonance is a special case of ______ vibrations, when frequency of the driving force is ______ natural frequency of the body.
Differentiate between the forced and resonant vibrations.
Why is a loud sound heard at resonance?
In following figure shows two tuning forks A and B of the same frequency mounted on two separate sound boxes with their open ends facing each other. The fork A is set into vibration.
- Describe your observation.
- State the principle illustrated by this experiment.

In Fig. A, B, C and D are four pendulums suspended from the same elastic string XY. The lengths of pendulum A and D are equal, while the length of pendulum B is shorter and of the pendulum C is longer. Pendulum A is set into vibrations.
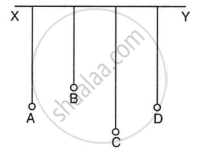
- What is your observation about the vibrations of pendulum D?
- Give reason for your observation in part (a).
- What type of vibrations take place in pendulums Band C?
- Give reason for the answer in part (c).
A vibrating tuning fork, held over an air column of a given length with its one end closed, produces a loud audible sound. Name the phenomenon responsible for it and explain the observation.
In following figure shows A, B , C and D represent test tube each of height 20 cm which are filled with water up to heights of 12 cm, 14 cm, 16cm and 18cm respectively. If a vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth if test tube D, a loud sound is heard.

- Describe the observations with the tubes A, B and C when the vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of these tubes.
- Give the reason for your observation in each case.
- State the principle illustrated by the above experiment.
When a troop crosses a suspension bridge, the soldiers are asked to break steps. Explain the reason.
Why are the stringed instruments like guitar provided with a hollow sound box?
How do you tune your radio set to a particular station ? Name the phenomenon involved in doing so and define it.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
A wire stretched between two fixed supports, is plucked exactly in the middle and then released. It executes (neglect the resistance of the medium) ______.
Resonant vibrations
natural vibrations
Damped vibrations
Forced vibrations
When a body vibrates under a periodic force, the vibrations of the body are ______.
natural vibrations
Damped vibrations
Forced vibrations
Resonant vibrations
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Sound EXERCISE - 7 (C) [Pages 172 - 174]
Name three characteristics of a musical sound.
- Which of the following quality determines the loudness of a sound wave?
- wavelength
- frequency and
- amplitude
- How is loudness related to the quantity mentioned above in part (a)?
If the amplitude of a wave is doubled, what will be the effect on its loudness?
Two waves of the same pitch have amplitudes in the ratio 1 : 3 What will be the ratio of their
- loudness,
- pitch?
How does the wave pattern of a loud note differ from that of a soft note? Draw a diagram.
Name the unit in which loudness of sound is measured.
Why is the loudness of the sound heard by a plucked wire increased when it is mounted on a sound board?
State the unit in which the intensity of a sound wave is measured.
State the unit in which the intensity of a sound wave is measured.
How is loudness of sound related to the intensity of wave producing it?
Comment on the statement 'loudness of sound is a subjective quantity, while intensity is an objective quantity.
The bells of a temple are big in size. Why?
Name the unit used to measure the sound level.
What is the safe limit of sound level in dB for our ears?
What is meant by noise pollution?
Name one source of sound causing noise pollution.
What determines the pitch of a sound?
Name the subjective property of sound related to its frequency.
Name and define the characteristic which enables one to distinguish two sounds of same loudness, but of different frequencies, given by the same instrument.
Draw a diagram to show the wave pattern of high pitch note and a low pitch note, but of the same loudness.
How is it possible to detect the filling of a bottle under a water tap by hearing the sound at a distance?
The frequencies of notes given by flute, guitar and trumpet are respectively 400 Hz, 200 Hz and 500 Hz. Which one of these has the highest pitch?
Complete the following sentences:
The pitch of sound increases if its frequency ______.
If the amplitude of a sound is halved, its loudness becomes ______.
The diagram below shows three different modes of vibration P, Q and R of the same string of a given length.
 |
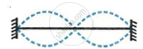 |
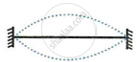 |
| P | Q | R |
- Which vibration will produce a louder sound and why?
- Which vibration will produce sound of maximum shrillness (or pitch) and why?
- What is the ratio of wavelength of vibrations P and R?
Name the characteristic which enables one to distinguish the sound of two musical instruments even if they are of the same pitch and same loudness.
How does the two sounds of same loudness and same pitch produced by different instruments differ? Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
Two identical guitars are played by two persons to give notes of the same loudness and pitch. Will they differ in quality? Give reason for your answer.
Two musical notes of the same pitch and same loudness are played on two different instruments. Their wave patterns are as shown in following Figure.

Explain why the wave patterns are different.
Which characteristics of sound makes it possible to recognize a person by his voice without seeing him?
State the factor that determine the pitch of a note.
State the factor that determine the loudness of the sound heard.
State the factor that determine the quality of the note.
Name the characteristic of the sound affected due to a change in its amplitude.
Name the characteristic of the sound affected due to a change in its wave form.
Name the characteristic of the sound affected due to a change in its frequency.
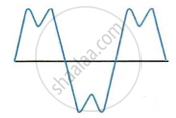
The sketches I to IV in following Figure show sound waves, all formed in the same time interval.
 |
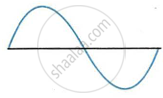 |
| I | II |
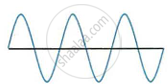 |
 |
| III | IV |
Which diagram shows
- a note from a musical instrument
- a soft (or feeble) note,
- a bass (low frequency) note.
Shows the wave patterns of three sounds A, B and C. Name the characteristic of sound which is same between
- A and B,
- B and C, and
- C and A.
| A | B | C |
 |
 |
 |
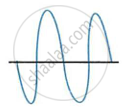
A microphone is connected to the Y-input of a C.R.O Three different sounds are made in turn in front of the microphone. Their traces (a), (b) and (c) produces on the screen are shown in following figure.
 |
 |
 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
- Which trace is due to the loudest sound? Give reason for your answer.
- Which trace is due for the sound with the lowest pitch? Explain your answer.
In what respect does the wave pattern of a noise and a music differ? Draw diagram to explain your answer.
State one difference between a musical note and a noise.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
By reducing the amplitude of a sound wave, its ______.
pitch increases
loudness decreases
loudness increases
pitch decreases
Two sounds of same loudness and same pitch produced by two different instruments differ in their ______.
amplitudes
frequencies
waveforms
all of the above.
Two sounds A and B are of same amplitude, same wave forms but of frequencies f and 2f respectively. Then ______.
B differs in quality from A
B is grave, A is shrill
B is shrill, A is grave
B is louder than A
Solutions for 7: Sound
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Sound Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Sound - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Sound
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 7 (Sound) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 Sound are Determination of Speed of Sound by the Method of Echo, Use of Echoes, Some Examples of Resonance, Sound, Difference Between the Sound and Light Waves, Reflection of Sound, Echoes, Natural Vibrations, Damped Vibrations, Forced Vibrations, Resonance, Demonstration of Resonance, Properties of Sounds, Loudness and Intensity, Pitch (or shrillness) and frequency, Audibility and Range, Quality (Or Timbre) and Wave Form, Noise Pollution, Noise and Music, Sound (Numerical), Determination of Speed of Sound by the Method of Echo, Use of Echoes, Some Examples of Resonance, Sound, Difference Between the Sound and Light Waves, Reflection of Sound, Echoes, Natural Vibrations, Damped Vibrations, Forced Vibrations, Resonance, Demonstration of Resonance, Properties of Sounds, Loudness and Intensity, Pitch (or shrillness) and frequency, Audibility and Range, Quality (Or Timbre) and Wave Form, Noise Pollution, Noise and Music, Sound (Numerical).
Using Selina Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Sound exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Sound Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
