Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
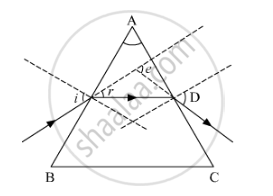
- A beam of monochromatic light undergoes minimum deviation through an equiangular prism, how does the beam pass through the prism, with respect to its base?
- If white light is used in the same way as in part (a) above, what change do you expect in the emergent beam?
- What conclusion do you draw about the nature of white light in part (b)?
Solution
- The beam of light pass parallel to the base.
- White light splits into its constituent colours i.e., spectrum is formed.
- White light is Polychromatic.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Study the following figure in which a student has marked the angle of incidence (∠i), angle of refraction (∠r), angle of emergence (∠e), angle of prism (∠A) and the angle of deviation (∠D). The correctly marked angles are
(a) ∠A and ∠i
(b) ∠A, ∠i and ∠r
(c) ∠A, ∠i, ∠e and ∠D
(d) ∠A, ∠i, ∠r and ∠D
(i) A ray of white light breaks up into its components while passing through a glass prism. Draw a ray diagram to show the path of rays.
(ii) Mark the least deviated colour in your diagram

(iii) Why do different coloured rays deviate differently in a prism?
As light rays emerge from a glass prism into air, are they refracted towards or away from the normal?
Out of air and glass, which is optically rarer? Give reason.
The wavelengths of violet and red light are 4000 Å and 8000 Å respectively. Which of the two has the higher frequency?
State two uses of ultraviolet radiation.
Match the Columns:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| The wavelength of red light | (a) 600 nm |
| (b) 700 nm | |
| (c) 500 nm |
Define dispersion of light.
Which of the following is a natural phenomenon which is caused by the dispersion of sunlight in the sky?
