Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- A beam of monochromatic light undergoes minimum deviation through an equiangular prism, how does the beam pass through the prism, with respect to its base?
- If white light is used in the same way as in part (a) above, what change do you expect in the emergent beam?
- What conclusion do you draw about the nature of white light in part (b)?
उत्तर
- The beam of light pass parallel to the base.
- White light splits into its constituent colours i.e., spectrum is formed.
- White light is Polychromatic.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
After tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass prism a student marked the angle of incidence (∠i), angle of refraction (∠r) angle of emergence (∠e) and the angle of deviation (∠D) as shown in the diagram. The correctly marked angles are :
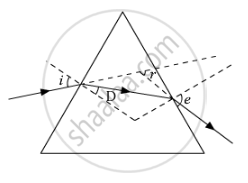
(A) ∠i and ∠r
(B) ∠i and ∠e
(C) ∠i, ∠e and ∠D
(D) ∠i, ∠r and ∠e
You are given a disc divided into seven sectors with colours violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red in them. What would be its colour when it is rotated rapidly?
The wavelengths of violet and red light are 4000 Å and 8000 Å respectively. Which of the two has the higher frequency?
The wavelength range of white light is ______.
What is the cause of the dispersion of white light through a glass prism? Draw a ray diagram to show the path of light when two identical glass prisms are arranged together in an inverted position with respect to each other and a narrow beam of white light is allowed to fall obliquely on one of the faces of the prisms.
State two properties of ultra-violet radiations which differ from visible light.
Define dispersion of light.
The phenomena of light involved in the formation of rainbow are ______.
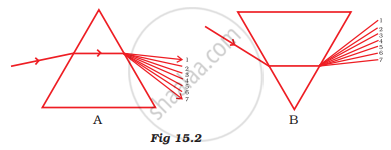
State the correct sequence (1-7) of colours in the spectrum formed by the prisms A and B, shown in Figure 15.2.