Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Force
2: Work, Energy and Power
3: Machines
LIGHT
4: Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
5: Refraction through a Lens
6: Spectrum
SOUND
7: Sound
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
8: Current Electricity
9: Household Circuits
▶ 10: Electro-Magnetism
HEAT
11: Calorimetry
MODERN PHYSICS
12: Radioactivity
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Electro-Magnetism Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Electro-Magnetism - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 10: Electro-Magnetism
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 10 of CISCE Selina for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 10 Electro-Magnetism EXERCISE-10 (A) [Pages 239 - 241]
By using a compass needle describe how can you demonstrate that there is a magnetic field around a current carrying conductor.
Draw a diagram showing the directions of three magnetic field lines due to a straight wire carrying current. Also show the direction of current in the wire.
How is the magnetic field due to a straight current carrying wire affected if current in wire is decreased?
How is the magnetic field due to a straight current carrying wire affected if current in wire is reversed?
State a law, which determines the direction of magnetic field around a current carrying wire.
A straight wire lying in a horizontal plane carries a current from north to south.
- What will be the direction of magnetic field at a point just underneath it?
- Name the law used to arrive at the answer in part (a).
What will happen to a compass needle when the compass is placed below a wire with needle parallel to it and a current is made to flow through the wire? Give a reason to justify your answer.
Draw a labelled diagram showing the three magnetic field lines of a loop carrying current. Mark the direction of current and the direction of magnetic field by arrows in your diagram.
A wire, bent into a circle, carries current in an anticlockwise direction. What polarity does this face of the coil exhibit?
What is the direction of magnetic field at the centre of a coil carrying current in clockwise ?
What is the direction of magnetic field at the centre of a coil carrying current in the anticlockwise direction?
Draw a diagram to represent the magnetic field lines along the axis of a current carrying solenoid. Mark arrows to show the direction of current in the solenoid and the direction of magnetic field lines.
Name and state the rule by which polarity at the ends of a current carrying solenoid is determined.
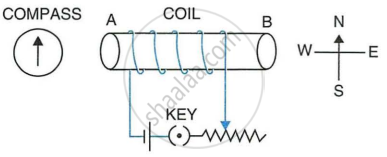
The adjacent diagram shows a small magnet placed near a solenoid AB. Current is switched on in the solenoid by pressing the key K.
- State the polarity at the ends A and B.
- Will the magnet be attracted or repelled? Give a reason for your answer.

The following diagram shows a spiral coil wound on a hollow carboard tube AB. A magnetic compass is placed close to it. Current is switched on by closing the key.
- What will be the polarity at the ends A and B?
- How will the compass needle be affected? Give reason.
State two ways by which the magnetic field due to a current carrying solenoid can be made stronger.
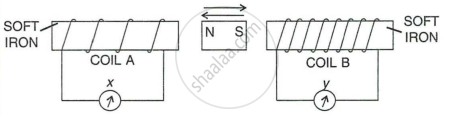
A magnet kept at the centre of two coils A and B is moved to and fro as shown in the diagram. The two galvanometers show deflection. State with a reason whether : x > y or x< y [x and y are magnitudes of deflection.]
Why does a current carrying freely suspended solenoid rest along a particular direction? State the direction in which it rests.
What effect will there be on a magnetic compass when it is brought near a current carrying solenoid?
How is the magnetic field due to a solenoid carrying current affected if a soft iron bar is introduced inside the solenoid?
Complete the following sentences :
When current flows in a wire, it creates ______.
On reversing the direction of the current in a wire, the magnetic field produced by it gets ______.
gets reversed in direction
increases in strength
decreases in strength
remains unchanged in strength and direction
A current carrying solenoid behaves like a ______.
A current carrying solenoid when freely suspended, it always rests in ______ direction.
You are required to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar by using a cell, an insulated coil of copper wire and a switch.
- Draw a circuit diagram to represent the process.
- Label the poles of the electromagnet.
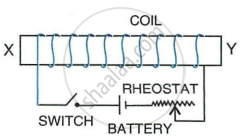
The following figure shows a coil wound around a soft iron bar XY.
- State the polarity at the ends X and Y as the switch is pressed.
- Suggest one way of increasing the strength of electromagnet so formed.
- What name is given to a cylindrical coil of diameter less than its length?
- If a piece of soft iron is placed inside the coil mentioned in part (a) and current is passed in the coil from a battery, what name is then given to the device so obtained?
- Give one use of the device mentioned in part (b).
Show with the aid of a diagram how a wire is wound on a U-shaped piece of soft iron in order to make it an electromagnet. Complete the circuit diagram and label the poles of the electromagnet.
What is an electromagnet?
Name two factors on which the strength of magnetic field of an electromagnet depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you.
In following figure shows the current flowing in the coil of wire wound around the soft iron horse shoe core.
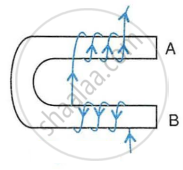
- State the polarities developed at the ends A and B.
- How will the polarity at the ends A and B change on reversing the direction of current?
- Suggest one way increase the strength of magnetic filed produced.
State two ways through which the strength of an electromagnet can be increased.
Name one device that uses an electromagnet.
State two advantages of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
State two differences between an electromagnet and a permanent magnet.
Why is soft iron used as the core of the electromagnet in an electric bell?
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
The incomplete diagram of an electric bell is given in Figure. Draw winding of coil on the core and complete the electric circuit in the diagram.
G-Gong, H-Hammer, A-Armature, C-Core, B-Battery.
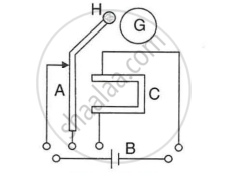
Name the material used for making the armature of an electric bell. Give a reason for your answer.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The present of magnetic field at a point can be detected by ______.
a strong magnet
a solenoid
a compass needle
a current carrying wire
On reversing the direction of the current in a wire, the magnetic field produced by it gets ______.
gets reversed in direction
increases in strength
decreases in strength
remains unchanged in strength and direction
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 10 Electro-Magnetism EXERCISE-10 (B) [Pages 246 - 247]
Name three factors on which the magnitude of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field depends and state how does the force depend on the factors stated by you.
State condition when magnitude of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is zero?
State condition when magnitude of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is maximum?
How will the direction of force be changed, if the current is reversed in the conductor placed in a magnetic field?
Name and state the law which is used to determine the direction of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field.
State Fleming's left handle rule.
State the unit of magnetic field in terms of the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field
A flat coil ABCD is freely suspended between the pole of U-shaped permanent magnet with the plane of coil parallel to the magnetic field.
What happens when a current is passed in the coil?
A flat coil ABCD is freely suspended between the pole of a U-shaped permanent magnet with the plane of coil parallel to the magnetic field.
When will coil come to rest?
A flat coil ABCD is freely suspended between the pole pieces of a U-shaped permanent magnet with the plane of coil parallel to the magnetic field.
When will the couple acting on the coil be
- maximum
- minimum?
A flat coil ABCD is freely suspended between the pole of a U-shaped permanent magnet with the plane of coil parallel to the magnetic field.
Name an instrument which makes use of the principle stated above.
A coil ABCD mounted on an axle is placed between the poles N and S of a permanent magnet as shown in Figure.
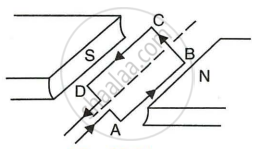
- In which direction will the coil begin to rotate when current is passed through the coil in direction ABCD by connecting a battery at the ends A and D of the coil?
- Why is a commutator necessary for continuous rotation of the coil?
- Complete the diagram with commutator, etc. for the flow of current in the coil?
What is an electric motor?
State the principle of an electric motor.
Draw a labelled diagram of a D.C. motor showing its main parts.
What energy conversion does take place during the working of a d.c. motor?
State two ways by which the speed of rotation of an electric motor can be increased.
Name two appliances in which an electric motor is used.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
In an electric motor the energy transformation is ______.
from electrical to chemical
from chemical to light
from mechanical to electrical
from electrical to mechanical
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE 10 Electro-Magnetism EXERCISE-10 (C) [Pages 258 - 260]
What is electromagnetic induction?
Describe one experiment to demonstrate the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
State Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction.
State two factors on which the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in a coil depend.
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
- How would you demonstrate that a momentary current can be obtained by the suitable use of a magnet, a coil of wire and a galvanometer?
- What is the source of energy associated with the current obtained in part (a)?
- Describe briefly one way producing an induced e.m.f?
- State one factor that determines the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in part (a) above.
- What factor determines the direction of induced e.m.f. in part (a) above?
Complete the following sentence:
The current induced in a closed circuit only if there is ______.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A current is started in a wire held near a loop of wire.
The current is switched off in a wire held near a loop of wire.
A magnet is moved through a loop of wire.
A loop of wire is held near a magnet.
A conductor is moved in a varying magnetic field. Name the law which determines the direction of current induced in the conductor.
What is Lenz’s law?
Why does it become more difficult to move a magnet towards a coil when the number of turns in the coil has been increased?
Explain why an induced current must flow in such a direction so as to oppose the change producing it.
Explain how does the Lenz's law show the conservation of energy in the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
The diagram in shows a coil of several turns of copper wire near a magnet NS. The coil is moved in the direction of arrow shown in the diagram.
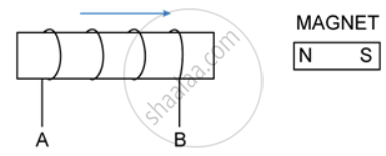
- In what direction does the induced current flow in the coil?
- Name the law used to arrive at the conclusion in part (i).
- How would the current in coil be altered if
- the coil has twice the number of turns,
- the coil was made to move three times fast?
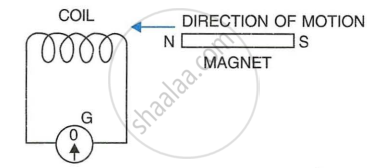
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Name and state the principle of a simple a.c. generator. What is its use?
What determines the frequency of a.c. produced in a generator?
Complete the sentence:
An a.c. generator changes the ______energy to ______ energy.
Draw a labelled diagram of a simple a.c. generator.
In an a.c. generator the speed at which the coil rotates is doubled. How would this affect
- the frequency of output voltage,
- the maximum output voltage is doubled.
Suggest two ways in an a.c. generator to produce a higher e.m.f.
What energy conversion does take place in a generator when it is in use?
State two dis-similarities between a d.c. motor and an a.c. generator.
Give two similarities an AC generator and a DC motor
State an important advantage of using alternating current (a.c.) over direct current (d.c.).
For what purpose are the transformers used?
On which type of current do transformers work?
State two factors on which the magnitude of an induced e.m.f. in the secondary coils of a transformer depends.
How are the e.m.f in the primary and secondary coils of a transformer related with the number of turns in these coils?
Draw a labelled diagram to show the various components of a step-up transformer.
Name the device used to transform 12 V a.c. to 200 V a.c.
Name the principal on which step up transformer works.
Draw a labelled diagram of a step-up transformer and explain how it works.
State two characteristics of the primary coil as compared to its secondary coil of a step-up transformer.
Draw a labelled diagram of a device you would use to transform 200 V a.c. to 15 V a.c. Name the device and explain how it works. Give its tow uses.
Name the coil of which the wire is thicker in a step up transformer. Give reason to your answer.
Name the coil of which the wire is thicker in a step down transformer. Give reason to your answer.
- Complete the following diagram of a transformer and name the parts labelled A and B.
- Name the part you have drawn to complete the diagram in part (a).
- What is the material of this part named above?
- Is this transformer a step up or step down? Give reason.
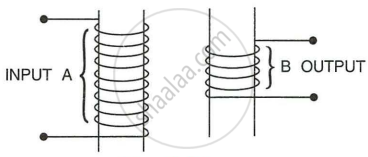
The following diagram shows the core of a transformer and its input and output connections.
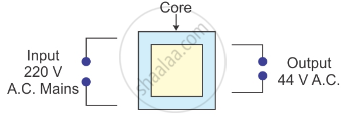
- State the material used for core and describe its structure.
- Complete the diagram of the transformer and connections by labelling all parts joined by you.
- Name the transformer: step-up or step down?
The output current of a transformer in which the voltage is stepped down is usually higher than the input current. Explain why.
The diagram below shows a magnetic needle kept just below the conductor AB which is kept in North South direction.

- In which direction will the needle deflect when the key _is closed?
- Why is the deflection produced?
- What will be the change in the deflection if the magnetic needle is taken just above the conductor AB?
- Name one device which works on this principle.
Why is the iron core of a transformer made laminated (thin sheets) instead of being in one solid piece?
Complete the following sentences:
In a step-up transformer, the number of turns in the primary are ______ than the number of turns in the secondary.
The transformer is used in ______ current circuits.
In a transformer, the frequency of A.C. voltage ______.
increase
decreases
remains same
How do the input and output powers in a transformer compare? State the assumption made.
Name two kind of energy loss in a transformer. How is it minimized?
Give two points of difference between a step-up transformer and step-down transformer.
Name the material of core in (a) an electric bell, (b) electromagnet, (c) a d.c. motor, (d) an a.c. generator and (e) a transformer.
Name the transformer used in the power generating station and state the function of the transformer.
Name the tranformer used in the power sub-station, state the function of each transfomer.
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The direction of induced current is obtained by ______.
Fleming's left hand rule
Clock rule
Right hand thumb rule
Fleming's right hand rule
In a step up transformer ______.
Ns = Np
Ns < Np
Ns > Np
nothing can be said
NUMERICALS
The magnetic flux through a coil having 100 turns decreases from 5 milli weber to zero in 5 second. Calculate the e.m.f. induced in the coil.
The primary coil of a transformer has 800 turns and the secondary coil has 8 turns. It is connected to a 220 V ac supply. What will be the output voltage?
A transformer is designed to work from a 240 V a.c. mains and to give a supply of 8 V to ring a house bell. The primary coil has 4800 turns. How many turns will be in the secondary coil?
The input and output voltage of a transformer are 220 V and 44 V respectively. Find: the turns ratio.
The input and output voltages of a transformer are 220 V and 44V respectively. Find the current in input circuit if the output current is 2 A.
Solutions for 10: Electro-Magnetism
![Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Electro-Magnetism Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Electro-Magnetism - Shaalaa.com](/images/physics-english-class-10-icse_6:4c973dd038c545c9a2b6db170ad2f542.jpg)
Selina solutions for Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Electro-Magnetism
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 10 (Electro-Magnetism) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 Electro-Magnetism are Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor, Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil), Right-hand Thumb Rule, Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid), Making of an Electromagnet, Permanent Magnet and Electromagnet, Applications of Electromagnets, Direct Current Motor, Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction, Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field, Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator, Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor, Types of Current, Transformers, Electromagnet, Frequency of A.C. in Household Supplies, Oersted's Experiment on the Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Types of Transformer, Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor, Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil), Right-hand Thumb Rule, Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid), Making of an Electromagnet, Permanent Magnet and Electromagnet, Applications of Electromagnets, Direct Current Motor, Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction, Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field, Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator, Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor, Types of Current, Transformers, Electromagnet, Frequency of A.C. in Household Supplies, Oersted's Experiment on the Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Types of Transformer.
Using Selina Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Electro-Magnetism exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 10, Electro-Magnetism Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Physics [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
