Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe one experiment to demonstrate the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
Solution
| (a) | 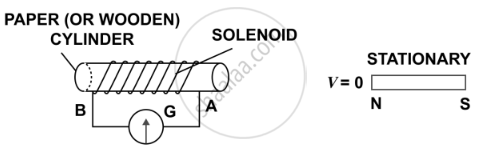 |
| (b) | 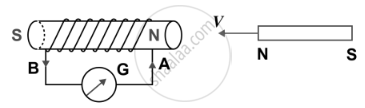 |
| (c) | 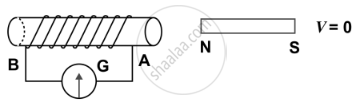 |
| (d) | 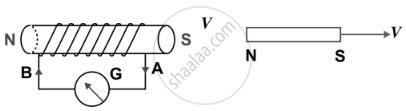 |
| (e) |  |
- When the magnet is stationary there is no deflection in galvanometer. The pointer read zero. [Fig. (a)]
- When the magnet with north pole facing the solenoid is moved towards the solenoid, the galvanometer shows a deflection towards the right showing that a current flows in the solenoid in the direction as shown in [Fig. (b)]
- As the motion of magnet stops, the pointer of the galvanometer comes to the zero position [Fig. (c)]. This shows that the current in the solenoid flows as long as the magnet is moving.
- If the magnet is moved away from the solenoid, the current again flows in the solenoid, but now in a direction opposite to that shown in [Fig. (b)] and therefore the pointer of the galvanometer deflects towards left [Fig. (d)].
- If the magnet is moved away rapidly i.e. with more velocity, the extent of deflection in the galvanometer increases although the direction of deflection remains the same. It shows that more current flows now.
- (vi) If the polarity of the magnet is reversed and then the magnet is brought towards the solenoid, the current in solenoid flows in the direction opposite to that shown in Fig. (b) and so the pointer of galvanometer deflect towards left [Fig. (e)].
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
The current is stopped in a wire held near a loop of wire .
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
The coil of a moving-coil galvanometer keeps on oscillating for a long time if it is deflected and released. If the ends of the coil are connected together, the oscillation stops at once. Explain.
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
A layer of atmosphere that reflects medium frequency radio waves which is ineffective during night, is ______.
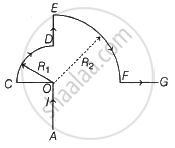
In the current carrying conductor (AOCDEFG) as shown, the magnetic induction at point O is ______.
(R1 and R2 are radii of CD and EF respectively. l = current in the loop, μ0 = permeability of free space)
The charge will flow through a galvanometer of resistance 200Ω connected to a 400Ω circular coil of 1000 turns wound on a wooden stick 20 mm in diameter, if a magnetic field B = 0.012 T parallel to the axis of the stick decreased suddenly to zero, is near ______.
