Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
Options
Charging of an electric conductor.
Production of magnetic field due to a current flowing through a coil.
Generation of a current in a coil due to relative motion between the coil and the magnet.
Motion of the coil around the axle in an electric motor.
Solution
Electromagnetic induction means generation of a current in a coil due to relative motion between the coil and the magnet.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The magnetic flux through a loop varies according to the relation Φ = 8t2 + 6t + C, where ‘C’ is constant, 'Φ' is in milliweber and 't' is in second. What is the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in the loop at t = 2 seconds.
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
The magnetic flux through a loop is varying according to a relation `phi = 6t^2 + 7t + 1` where `phi` is in milliweber and t is in second. What is the e.m.f. induced in the loop at t = 2 second?
State three ways in which the strength of an electromagnet can be increased.
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
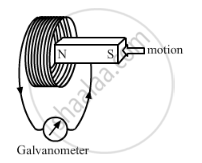
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
The current is stopped in a wire held near a loop of wire .
Welders wear special goggles or face masks with glass windows to protect their eyes from electromagnetic radiations. Name the radiations and write the range of their frequency.
Consider the energy density in a solenoid at its centre and that near its ends. Which of the two is greater?
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
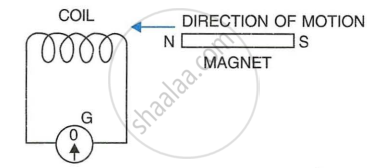
Fig. shows a simple form of an A.C. generator.

(a) Name the parts labeled A and B.
(b) What would be the effect of doubling the number of turns on the coil if the speed of rotation remains unchanged?
(c) Which of the output terminals is positive if the coil is rotating in the
direction shown in the diagram (anticlockwise)?
( d ) What is the position of the rotating coil when p.d. across its ends is zero? Explain why p.d. is zero when the coil is at this position .
(e) Sketch a graph showing how the p.d. across the ends of the rotating coil varies with time for an A.C. dynamo.
( f) On th e same sheet of paper and vertically below the first graph using the same time scale, sketch graphs to show the effect of
(i) Doubling the speed of rotation and at the same time keeping
the field and the number of turns constant,
(ii ) Doubling the number of turns on the coil and at the same time
doubling the speed of rotation of the coil, keeping th e speed
constant.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
D.C. motor ______.
A transformer has 400 turns in the primary winding and 10 turns in the secondary winding. The primary e.m.f. is 250 V and the primary current is 2.0 A. calculate:
(a) The secondary voltage,
(b) The secondary current, assuming 100% efficiency.
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
What is an electromagnet? List any two uses.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
You have been provided with a solenoid AB.
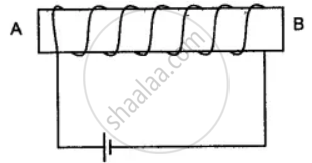
(i) What is the polarity at end A?
(ii) Give one advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet.
Using Ampere's law, obtain an expression for the magnetic induction near a current-carrying straight infinitely long wire.
Fleming's left hand rule : electric current : : Fleming's right hand rule : _______
What for an inductor is used? Give some examples.
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
A coil of 200 turns carries a current of 0.4 A. If the magnetic flux of 4 mWb is linked with each turn of the coil, find the inductance of the coil.
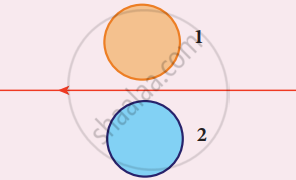
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
A generator has an e.m.f. of 440 Volt and internal resistance of 4000 hm. Its terminals are connected to a load of 4000 ohm. The voltage across the load is ______.
We can induce the current in a coil by ____________.
Induced current flows through a coil ______.
For making a strong electromagnet the material of the core should be ______.
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
One solenoid is centered inside another. The outer one has a length of 50.0 cm and contains 6750 coils, while the coaxial inner solenoid is 3.0 cm long and π cm2 in area and contains 150 coils. The current in the outer solenoid is changing at 3000 A/s. The emf induced in the inner solenoid is ______ V.
(Round off to two decimal places.)
The primary of a transformer has 400 turns while the secondary has 2000 turns. If the power output from the secondary at 1000 Vis 12 kW, what is the primary voltage?
