Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The magnetic flux through a loop varies according to the relation Φ = 8t2 + 6t + C, where ‘C’ is constant, 'Φ' is in milliweber and 't' is in second. What is the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in the loop at t = 2 seconds.
Solution
Magnetic flux through the coil is given by relation
Φ = 8t2 + 6t + c (where c is constant) (i)
To find the magnitude of the induced e.m.f. ‘e’ in the loop at t = 2 seconds, we know that `e=|(dphi)/dt|`
Differentiating equation (i) w.r.t. t we get,
e = 16t + 6
e = 16 × (2) + 6
e = 38 millivolt = 0.038 volt
Hence, the magnitude of induced e.m.f. is 0.038 volt.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Electric field intensity in free space at a distance ‘r’ outside the charged conducting sphere of radius ‘R’ in terms of surface charge density ‘ a ’ is............................
(a)`sigma / in_0[R/r]^2`
(b)`in_0/sigma[R/r]^2`
(c)`R/r[sigma/in_0]^2`
(d)`R/sigma[r/in_0]^2`
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
The device used for producing electric current is called _________.
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s−1, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 × 10−4 Wb m−2.
- What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire?
- What is the direction of the emf?
- Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
Prove theoretically (electromagnetic induction) `e = (dphi)/(dt)`
A circular coil of cross-sectional area 200 cm2 and 20 turns is rotated about the vertical diameter with angular speed of 50 rad s−1 in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 3.0 × 10−2T. Calculate the maximum value of the current in the coil.
An emf of 2V is induced in a coil when the current in it is changed from 0A to 10A in 0·40 sec. Find the coefficient of self-inductance of the coil.
State three ways in which the strength of an electromagnet can be increased.
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
Write some of the important uses of electromagnets.
The most suitable material for making the core of an electromagnet is:
(a) soft iron
(b) brass
(c) aluminium
(d) steel
What condition is necessary for the production of current by electromagnetic induction?
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
When current is 'switched on' and 'switched off' in a coil, a current is induced in another coil kept near it. What is this phenomenon known as?
Name one device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
The current is stopped in a wire held near a loop of wire .
In which of the following case does the electromagnetic induction occur?
A magnet is moved through a loop of wire .
Name and state the law which determines the direction of induced current.
or
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
Welders wear special goggles or face masks with glass windows to protect their eyes from electromagnetic radiations. Name the radiations and write the range of their frequency.
Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop.
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
A conducting rod is moved with a constant velocity v in a magnetic field. A potential difference appears across the two ends _____________ .
L, C and R represent the physical quantities inductance, capacitance and resistance respectively. Which of the following combinations have dimensions of frequency?
(a) `1/(RC)`
(b) `R/L`
(c) `1/sqrt(LC)`
(d) C/L
Calculate the dimensions of (a) \[\int \overrightarrow{E} . d \overrightarrow{l,}\] (b) vBl and (c) \[\frac{d \Phi_B}{dt}.\] The symbols have their usual meaning.
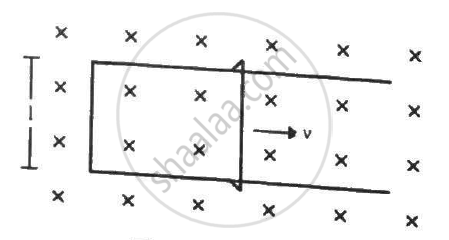
Figure shows a long U-shaped wire of width l placed in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A wire of length l is slid on the U-shaped wire with a constant velocity v towards right. The resistance of all the wires is r per unit length. At t = 0, the sliding wire is close to the left edge of the U-shaped wire. (a) Calculate the force needed to keep the sliding wire moving with a constant velocity v. (b) If the force needed just after t = 0 is F0, find the time at which the force needed will be F0/2.0
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-up transformer.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
D.C. motor ______.
Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electromagnet is made.
Draw a labelled diagram to make an electromagnet from a soft iron bar. Mark the polarity at its ends in your diagram. What precaution would you observe while making it?
The diagram shows a rectangular coil ABCD, suspended freely between the concave pole pieces of a permanent horseshoe magnet, such that the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field.

(i) State your observation, when current is switched on.
(ii) Give an explanation for your observation in (i).
(iii) State the rule, which will help you to find the motion of rotation of coil.
(iv) In which position will the coil ultimately come to rest?
(v) State four ways of increasing the magnitude of force acting on the coil.
State the condition at which we say the two coils kept close to each other are perfectly coupled with each other.
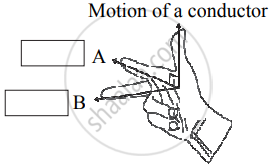
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
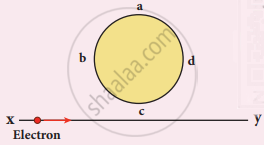
An electron moves on a straight-line path XY as shown in the figure. The coil abcd is adjacent to the path of the electron. What will be the direction of the current, if any, induced in the coil?
A square coil of side 30 cm with 500 turns is kept in a uniform magnetic field of 0.4 T. The plane of the coil is inclined at an angle of 30° to the field. Calculate the magnetic flux through the coil.
The magnetic flux passing through a coil perpendicular to its plane is a function of time and is given by OB = (2t3 + 4t2 + 8t + 8) Wb. If the resistance of the coil is 5 Ω, determine the induced current through the coil at a time t = 3 second.
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
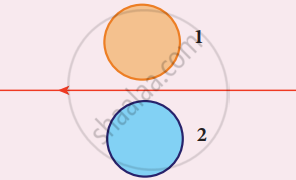
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
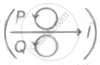
Metal rings P and Q are lying in the same plane, where current I is increasing steadily. The induced current in metal rings is shown correctly in figure.
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
The condition for the praenomen of electromagnetic induction is that there must be a relative motion between ____________.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
What is the principle which Ansari Sir is trying to demonstrate?
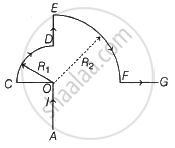
In the current carrying conductor (AOCDEFG) as shown, the magnetic induction at point O is ______.
(R1 and R2 are radii of CD and EF respectively. l = current in the loop, μ0 = permeability of free space)