Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Electric field intensity in free space at a distance ‘r’ outside the charged conducting sphere of radius ‘R’ in terms of surface charge density ‘ a ’ is............................
(a)`sigma / in_0[R/r]^2`
(b)`in_0/sigma[R/r]^2`
(c)`R/r[sigma/in_0]^2`
(d)`R/sigma[r/in_0]^2`
Solution
(a) `sigma / in_0[R/r]^2`
Electric field intensity in the free space outside the charged conducting sphere in terms of surface charged density is given as
`E=sigma / in_0[R/r]^2`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A solenoid of length 1.5 m and 4 cm in diameter possesses 10 turns per metre. A current of 5 A is flowing through it. The magnetic induction at a point inside the solenoid along the axis is ............................. .
(μ0 = 4π × 10-7 Wb/Am)
- π × 10-5 T
- 2π × 10-5 T
- 3π × 10-5 T
- 4π × 10-5 T
State three differences between direct current and alternating current.
A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s−1 in a direction normal to the
- longer side,
- shorter side of the loop?
For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
It is desired to measure the magnitude of field between the poles of a powerful loud speaker magnet. A small flat search coil of area 2 cm2 with 25 closely wound turns, is positioned normal to the field direction, and then quickly snatched out of the field region. Equivalently, one can give it a quick 90° turn to bring its plane parallel to the field direction. The total charge flown in the coil (measured by a ballistic galvanometer connected to coil) is 7.5 mC. The combined resistance of the coil and the galvanometer is 0.50 Ω. Estimate the field strength of magnet.
Explain why, an electromagnet is called a temporary magnet.
State the factors on which the strength of an electromagnet depends. How does it depend on these factors?
The direction of current in the coil at one end of an electromagnet is clockwise. This end of the electromagnet will be:
(a) north pole
(b) east pole
(c) south pole
(d) west pole
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
When current is 'switched on' and 'switched off' in a coil, a current is induced in another coil kept near it. What is this phenomenon known as?
Name one device which works on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction.
An induced current is produced when a magnet is moved into a coil. The magnitude of induced current does not depend on:
(a) the speed with which the magnet is moved
(b) the number of turns of the coil
(c) the resistivity of the wire of the coil
(d) the strength of the magnet
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
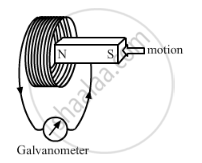
() What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
(2) State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
(3) The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
How is the working of an electric bell affected, if alternating current be used instead of direct current?
- What kind of energy change takes place when a magnet is moved towards a coil having a galvanometer at its ends?
- Name the phenomenon.
When Puja, a student of 10th class, watched her mother washing clothes in the open, she observed coloured soap bubbles and was curious to know why the soap bubbles appear coloured. In the evening when her father, an engineer by profession, came home, she asked him this question. Her father explained to her the basic phenomenon of physics due to which the soap bubbles appear coloured.
(a) What according to you are the values displayed by Puja and her father?
(b) State the phenomenon of light involved in the formation of coloured soap bubbles.
Electromagnetic induction means ______.
A conducting square loop of side l and resistance R moves in its plane with a uniform velocity v perpendicular to one of its sides. A uniform and constant magnetic field Bexists along the perpendicular to the plane of the loop as shown in figure. The current induced in the loop is _____________ .
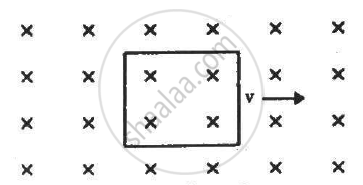
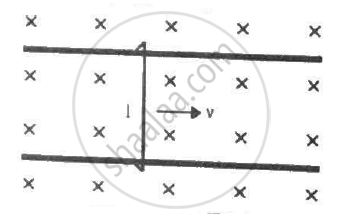
Figure shows a wire sliding on two parallel, conducting rails placed at a separation l. A magnetic field B exists in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the rails. What force is necessary to keep the wire moving at a constant velocity v?
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-down transformer.
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-up transformer.
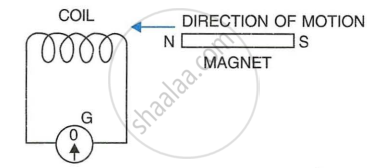
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
D.C. motor ______.
Fill in the blanks by writing (i) Only soft iron, (ii) Only steel, (iii) Both soft-iron and steel for the material of core and/or magnet.
Transformer______.
A coil has a self-inductance of 0·05 Henry. Find the magnitude of the emf induced in it when the current flowing through it is changing at the rate of 100 As-1.
State Fleming’s Right Hand Rule.
Answer the following:
State the principles of the electric motor and electric generator.
What is an electromagnet? List any two uses.
Draw a labelled diagram to show how an electromagnet is made.
State the purpose of soft iron core used in making an electromagnet.
List two ways of increasing the strength of an electromagnet if the material of the electromagnet is fixed.
List some of the practical applications of an electromagnet.
Why soft iron is preferred to be used as the core of the electromagnet of an electric bell?
The diagram shows a rectangular coil ABCD, suspended freely between the concave pole pieces of a permanent horseshoe magnet, such that the plane of the coil is parallel to the magnetic field.

(i) State your observation, when current is switched on.
(ii) Give an explanation for your observation in (i).
(iii) State the rule, which will help you to find the motion of rotation of coil.
(iv) In which position will the coil ultimately come to rest?
(v) State four ways of increasing the magnitude of force acting on the coil.
The right-hand thumb rule is also called _______ rule.
A thin semi-circular conducting ring (PQR) of radius r is falling with its plane vertical in a horizontal magnetic field B, as shown in the figure.
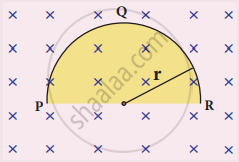
The potential difference developed across the ring when its speed v , is
Establish the fact that the relative motion between the coil and the magnet induces an emf in the coil of a closed circuit.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
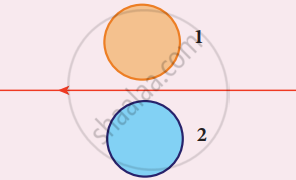
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
An alternating emf of 0.2 V is applied across an L-C-R series circuit having R = 4Q, C = 80µF, and L = 200 mH. At resonance the voltage drop across the inductor is
There is a uniform magnetic field directed perpendicular and into the plane of the paper. An irregular shaped conducting loop is slowly changing into a circular loop in the plane of the paper. Then ______.
The condition for the praenomen of electromagnetic induction is that there must be a relative motion between ____________.
The instrument that use to defect electric current in the circuit is known as ____________.
Ansari Sir was demonstrating an experiment in his class with the setup as shown in the figure below.

A magnet is attached to a spring. The magnet can go in and out of the stationary coil. He lifted the Magnet and released it to make it oscillate through the coil.
Based on your understanding of the phenomenon, answer the following question.
What is the principle which Ansari Sir is trying to demonstrate?
If the sun radiates energy at the rate of 3.6 × 1033 ergs/sec the rate at which the sun is loosing mass is given by ______.
Sea turtles return to their birth beach many decades after they were born due to ______.
A coil of one turn is made of a wire of certain length and then from the same length, a coil of two turns is made. If the same current is passed in both the cases, then the ratio of the magnetic inductions at their centres will be:
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
An expression for oscillating electric field in a plane electromagnetic wave is given as Ez = 300 sin(5π × 103x - 3π × 1011t)Vm-1 Then, the value of magnetic field amplitude will be ______. (Given: speed of light in Vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
