Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
Solution
Consider a straight conducting rod AB of length l in a uniform magnetic field `vec"B"` which is directed perpendicularly into the plane of the paper. The length of the rod is normal to the magnetic field. Let the rod move with a constant velocity `vec"v"` towards right side.
When the rod moves, the free electrons present in it also move with same velocity `vec"v"` in `vec"B"`. As a result, the Lorentz force acts on free electrons in the direction from B to A and is given by the relation
`vec"F"_"B" = - "e"(vec"v" xx vec"B")` ....(1)
The action of this Lorentz force is to accumulate the free electrons at the end A. This accumulation of free electrons produces a potential difference across the rod which in turn establishes an electric field E directed along BA. Due to the electric field E, the coulomb force starts acting on the free electrons along AB and is given by
`vec"F"_"E" = - "e"vec"E"` ....(2)
The magnitude of the electric field `vec"E"` keeps on increasing as long as the accumulation of electrons at the end A continues. The force `vec"F"_"E"` also increases until equilibrium is reached. At equilibrium, the magnetic Lorentz force `vec"F"_"B"` and the coulomb force `vec"F"_"E"` balance each other and no further accumulation of free electrons at the end A takes place, i.e.,
`|vec"F"_"B"| = |vec"F"_"E"|`
`|-"e" (vec"v" xx vec"B")| = |-"e" vec"E"|`
vB sin 90° = E
vB = E ……. (3)
The potential difference between two ends of the rod is
(a) 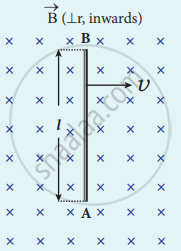
(b)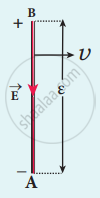
Motional emf from Lorentz force
V = El
V = vBl
Thus the Lorentz force on the free electrons is responsible to maintain this potential difference and hence produces an emf.
ε = Blv ….. (4)
As this emf is produced due to the movement of the rod, it is often called as motional emf.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State Fleming’s right-hand rule.
How does an electromagnet differ forma permanent magnet?
State whether the following statement are true or false:
A motor works on the principle electric generator?
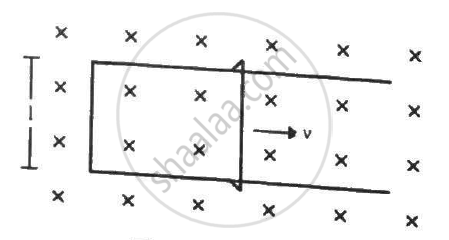
Figure shows a long U-shaped wire of width l placed in a perpendicular magnetic field B. A wire of length l is slid on the U-shaped wire with a constant velocity v towards right. The resistance of all the wires is r per unit length. At t = 0, the sliding wire is close to the left edge of the U-shaped wire. (a) Calculate the force needed to keep the sliding wire moving with a constant velocity v. (b) If the force needed just after t = 0 is F0, find the time at which the force needed will be F0/2.0
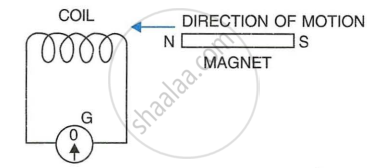
The following diagram shows a fixed coil of several turns connected to a center zero galvanometer G and a magnet NS which can move in the direction shown in the diagram.
- Describe the observation in the galvanometer if
- The magnet is moved rapidly,
- The magnet is kept still after it has moved into the coil
- The magnet is then rapidly pulled out the coil.
- How would the observation in (i) of part (a) change if a more powerful magnet is used?
Using Ampere's law, obtain an expression for the magnetic induction near a current-carrying straight infinitely long wire.
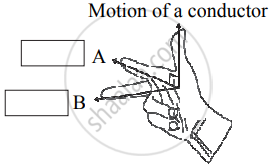
Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
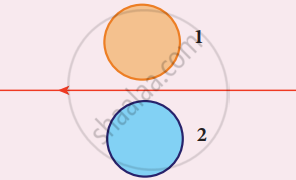
Using Lenz’s law, predict the direction of induced current in conducting rings 1 and 2 when the current in the wire is steadily decreasing.
A 0.4 m wire, stretched horizontally, carries an electric current of 15 A, in a magnetic field whose magnetic field intensity is 0.1 N/Am. What is the magnitude of the wire?
Which type of force is experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field?
